Polymers and fibres are giant molecules of organic compounds. Polymers and fibres are formed when small molecules called monomers join together to form large molecules called polymers at high temperatures and pressures. This process is called polymerization.
Polymers and fibres are either:
(a)Natural polymers and fibres
(b)Synthetic polymers and fibres
Natural polymers and fibres are found in living things(plants and animals) Natural polymers/fibres include:
-proteins/polypeptides making amino acids in animals
-cellulose that make cotton,wool,paper and silk
-Starch that come from glucose
-Fats and oils
-Rubber from latex in rubber trees.
Synthetic polymers and fibres are man-made. They include:
-polyethene
-polychloroethene
-polyphenylethene(polystyrene)
-Terylene(Dacron)
-Nylon-6,6
-Perspex(artificial glass)
Synthetic polymers and fibres have the following characteristic advantages over natural polymers
1. They are light and portable
2. They are easy to manufacture.
3. They can easily be molded into shape of choice.
4. They are resistant to corrosion, water, air , acids, bases and salts.
5. They are comparatively cheap, affordable, colourful and aesthetic
Synthetic polymers and fibres however have the following disadvantages over natural polymers
- They are non-biodegradable and hence cause environmental pollution during disposal
- They give out highly poisonous gases when burnt like chlorine/carbon(II)oxide
- Some on burning produce Carbon(IV)oxide. Carbon(IV)oxide is a green house gas that cause global warming.
- Compared to some metals, they are poor conductors of heat,electricity and have lower tensile strength.
To reduce environmental pollution from synthetic polymers and fibres, the followitn methods of disposal should be used:
1.Recycling: Once produced all synthetic polymers and fibres should be recycled to a new product. This prevents accumulation of the synthetic polymers and fibres in the environment.
2.Production of biodegradable synthetic polymers and fibres that rot away.
There are two types of polymerization:
(a)addition polymerization
(b)condensation polymerization
(a)addition polymerization
Addition polymerization is the process where a small unsaturated monomer (alkene ) molecule join together to form a large saturated molecule. Only alkenes undergo addition polymerization.
Addition polymers are named from the alkene/monomer making the polymer and adding the prefix “poly” before the name of monomer to form a polyalkene
During addition polymerization
(i)the double bond in alkenes break
(ii)free radicals are formed
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule. The more collisions the larger the molecule.
Examples of addition polymerization
1.Formation of Polyethene
Polyethene is an addition polymer formed when ethene molecule/monomer join together to form a large molecule/polymer at high temperatures and pressure.
During polymerization:
(i)many molecules are brought nearer to each other by the high pressure(which reduces the volume occupied by reacting paticles)
H H H H H H H H
C = C + C = C + C = C + C = C + …
H H H H H H H H
Ethene + Ethene + Ethene + Ethene + …
(ii)the double bond joining the ethane molecule break to free readicals
H H H H H H H H
•C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + …
H H H H H H H H
Ethene radical + Ethene radical + Ethene radical + Ethene radical + …
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule
H H H H H H H H lone pair of electrons
•C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C• + …
H H H H H H H H
Lone pair of electrons can be used to join more monomers to form longer polyethene.
Polyethene molecule can be represented as:
H H H H H H H H extension of
molecule/polymer
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C- + …
H H H H H H H H
Since the molecule is a repetition of one monomer, then the polymer is:
H H
( C – C )n
H H
Where n is the number of monomers in the polymer. The number of monomers in the polymer can be determined from the molar mass of the polymer and monomer from the relationship:
Number of monomers/repeating units in monomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
Examples
Polythene has a molar mass of 4760.Calculate the number of ethene molecules in the polymer(C=12.0, H=1.0 )
Number of monomers/repeating units in polyomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
=> Molar mass ethene (C2H4 )= 28 Molar mass polyethene = 4760
Substituting 4760 = 170 ethene molecules
28
The commercial name of polyethene is polythene. It is an elastic, tough, transparent and durable plastic. Polythene is used:
(i)in making plastic bag
(ii)bowls and plastic bags
(iii)packaging materials
2.Formation of Polychlorethene
Polychloroethene is an addition polymer formed when chloroethene molecule/monomer join together to form a large molecule/polymer at high temperatures and pressure.
During polymerization:
(i)many molecules are brought nearer to each other by the high pressure(which reduces the volume occupied by reacting particles)
H H H H H H H H
C = C + C = C + C = C + C = C + …
H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl
chloroethene + chloroethene + chloroethene + chloroethene + …
(ii)the double bond joining the chloroethene molecule break to free radicals
H H H H H H H H
•C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + …
H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule
H H H H H H H H lone pair of electrons
•C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C• + …
H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl
Lone pair of electrons can be used to join more monomers to form longer polychloroethene.
Polychloroethene molecule can be represented as:
H H H H H H H H extension of
molecule/polymer
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C- + …
H Cl H Cl H Cl H Cl
Since the molecule is a repetition of one monomer, then the polymer is:
H H
( C – C )n
H Cl
Examples
Polychlorothene has a molar mass of 4760.Calculate the number of chlorethene molecules in the polymer(C=12.0, H=1.0,Cl=35.5 )
Number of monomers/repeating units in monomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
=> Molar mass ethene (C2H3Cl )= 62.5 Molar mass polyethene = 4760
Substituting 4760 = 77.16 => 77 polychloroethene molecules(whole number)
62.5
The commercial name of polychloroethene is polyvinylchloride(PVC). It is a tough, non-transparent and durable plastic. PVC is used:
(i)in making plastic rope
(ii)water pipes
(iii)crates and boxes
3.Formation of Polyphenylethene
Polyphenylethene is an addition polymer formed when phenylethene molecule/monomer join together to form a large molecule/polymer at high temperatures and pressure.
During polymerization:
(i)many molecules are brought nearer to each other by the high pressure(which reduces the volume occupied by reacting particles)
H H H H H H H H
C = C + C = C + C = C + C = C + …
H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5
phenylethene + phenylethene + phenylethene + phenylethene + …
(ii)the double bond joining the phenylethene molecule break to free radicals
H H H H H H H H
•C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + …
H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule
H H H H H H H H lone pair of electrons
• C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C • + …
H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5
Lone pair of electrons can be used to join more monomers to form longer polyphenylethene.
Polyphenylethene molecule can be represented as:
H H H H H H H H
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C –
H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5 H C6H5
Since the molecule is a repetition of one monomer, then the polymer is:
H H
( C – C )n
H C6H5
Examples
Polyphenylthene has a molar mass of 4760.Calculate the number of phenylethene molecules in the polymer(C=12.0, H=1.0, )
Number of monomers/repeating units in monomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
=> Molar mass ethene (C8H8 )= 104 Molar mass polyethene = 4760
Substituting 4760 = 45.7692 =>45 polyphenylethene molecules(whole number)
104
The commercial name of polyphenylethene is polystyrene. It is a very light durable plastic. Polystyrene is used:
(i)in making packaging material for carrying delicate items like computers, radion,calculators.
(ii)ceiling tiles
(iii)clothe linings
4.Formation of Polypropene
Polypropene is an addition polymer formed when propene molecule/monomer join together to form a large molecule/polymer at high temperatures and pressure.
During polymerization:
(i)many molecules are brought nearer to each other by the high pressure(which reduces the volume occupied by reacting particles)
H H H H H H H H
C = C + C = C + C = C + C = C + …
H CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H CH3
propene + propene + propene + propene + …
(ii)the double bond joining the phenylethene molecule break to free radicals
H H H H H H H H
•C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + …
H CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H CH3
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule
H H H H H H H H lone pair of electrons
• C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C • + …
H CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H CH3
Lone pair of electrons can be used to join more monomers to form longer propene.
propene molecule can be represented as:
H H H H H H H H
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C –
H CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H CH3
Since the molecule is a repetition of one monomer, then the polymer is:
H H
( C – C )n
H CH3
Examples
Polypropene has a molar mass of 4760.Calculate the number of propene molecules in the polymer(C=12.0, H=1.0, )
Number of monomers/repeating units in monomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
=> Molar mass propene (C3H8 )= 44 Molar mass polyethene = 4760
Substituting 4760 = 108.1818 =>108 propene molecules(whole number)
44
The commercial name of polyphenylethene is polystyrene. It is a very light durable plastic. Polystyrene is used:
(i)in making packaging material for carrying delicate items like computers, radion,calculators.
(ii)ceiling tiles
(iii)clothe linings
5.Formation of Polytetrafluorothene
Polytetrafluorothene is an addition polymer formed when tetrafluoroethene molecule/monomer join together to form a large molecule/polymer at high temperatures and pressure.
During polymerization:
(i)many molecules are brought nearer to each other by the high pressure(which reduces the volume occupied by reacting particles)
F F F F F F F F
C = C + C = C + C = C + C = C + …
F F F F F F F F
tetrafluoroethene + tetrafluoroethene+ tetrafluoroethene+ tetrafluoroethene + …
(ii)the double bond joining the tetrafluoroethene molecule break to free radicals
F F F F F F F F
•C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + •C – C• + …
F F F F F F F F
(iii)the free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule
F F F F F F F F lone pair of electrons
•C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C• + …
F F F F F F F F
Lone pair of electrons can be used to join more monomers to form longer polytetrafluoroethene.
polytetrafluoroethene molecule can be represented as:
F F F F F F F F extension of
molecule/polymer
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C- + …
F F F F F F F F
Since the molecule is a repetition of one monomer, then the polymer is:
F F
( C – C )n
F F
Examples
Polytetrafluorothene has a molar mass of 4760.Calculate the number of tetrafluoroethene molecules in the polymer(C=12.0, ,F=19 )
Number of monomers/repeating units in monomer = Molar mass polymer
Molar mass monomer
=> Molar mass ethene (C2F4 )= 62.5 Molar mass polyethene = 4760
Substituting 4760 = 77.16 => 77 polychloroethene molecules(whole number)
62.5
The commercial name of polytetrafluorethene(P.T.F.E) is Teflon(P.T.F.E). It is a tough, non-transparent and durable plastic. PVC is used:
(i)in making plastic rope
(ii)water pipes
(iii)crates and boxes
5.Formation of rubber from Latex
Natural rubber is obtained from rubber trees.
During harvesting an incision is made on the rubber tree to produce a milky white substance called latex.
Latex is a mixture of rubber and lots of water.
The latex is then added an acid to coagulate the rubber.
Natural rubber is a polymer of 2-methylbut-1,3-diene ;
H CH3 H H
CH2=C (CH3) CH = CH2 H – C = C – C = C – H
During natural polymerization to rubber, one double C=C bond break to self add to another molecule. The double bond remaining move to carbon “2” thus;
H CH3 H H H CH3 H H
– C – C = C – C – C – C = C – C –
H H H H
Generally the structure of rubber is thus;
H CH3 H H
-(- C – C = C – C -)n–
H H
Pure rubber is soft and sticky. It is used to make erasers, car tyres. Most of it is vulcanized. Vulcanization is the process of heating rubber with sulphur to make it harder/tougher.
During vulcanization the sulphur atoms form a cross link between chains of rubber molecules/polymers. This decreases the number of C=C double bonds in the polymer.
| Sulphur atoms make cross link between polymers |
H CH3 H H H CH3 H H
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C –
H S H H S H
H CH3 S H H CH3 S H
– C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C –
H H H H H H
Vulcanized rubber is used to make tyres, shoes and valves.
6.Formation of synthetic rubber
Synthetic rubber is able to resist action of oil,abrasion and organic solvents which rubber cannot.
Common synthetic rubber is a polymer of 2-chlorobut-1,3-diene ;
H Cl H H
CH2=C (Cl CH = CH2 H – C = C – C = C – H
During polymerization to synthetic rubber, one double C=C bond is broken to self add to another molecule. The double bond remaining move to carbon “2” thus;
H Cl H H H Cl H H
– C – C = C – C – C – C = C – C –
H H H H
Generally the structure of rubber is thus;
H Cl H H
-(- C – C = C – C -)n–
H H
Rubber is thus strengthened through vulcanization and manufacture of synthetic rubber.
(b)Condensation polymerization
Condensation polymerization is the process where two or more small monomers join together to form a larger molecule by elimination/removal of a simple molecule. (usually water).
Condensation polymers acquire a different name from the monomers because the two monomers are two different compounds
During condensation polymerization:
(i)the two monomers are brought together by high pressure to reduce distance between them.
(ii)monomers realign themselves at the functional group.
(iii)from each functional group an element is removed so as to form simple molecule (of usually H2O/HCl)
(iv)the two monomers join without the simple molecule of H2O/HCl
Examples of condensation polymerization
1.Formation of Nylon-6,6
Method 1: Nylon-6,6 can be made from the condensation polymerization of hexan-1,6-dioic acid with hexan-1,6-diamine.Amines are a group of homologous series with a general formula R-NH2 and thus -NH2 as the functionalgroup.
During the formation of Nylon-6,6:
(i)the two monomers are brought together by high pressure to reduce distance between them and realign themselves at the functional groups.
O O H H
H- O – C – (CH2 ) 4 – C – O – H + H –N – (CH2) 6 – N – H
(iii)from each functional group an element is removed so as to form a molecule of H2O and the two monomers join at the linkage .
O O H H
H- O – C – (CH2 ) 4 – C – N – (CH2) 6 – N – H + H 2O
.
Polymer bond linkage
Nylon-6,6 derive its name from the two monomers each with six carbon chain
Method 2: Nylon-6,6 can be made from the condensation polymerization of hexan-1,6-dioyl dichloride with hexan-1,6-diamine.
Hexan-1,6-dioyl dichloride belong to a group of homologous series with a general formula R-OCland thus -OCl as the functionalgroup.
The R-OCl is formed when the “OH” in R-OOH/alkanoic acid is replaced by Cl/chlorine/Halogen
During the formation of Nylon-6,6:
(i)the two monomers are brought together by high pressure to reduce distance between them and realign themselves at the functional groups.
O O H H
Cl – C – (CH2 ) 4 – C – Cl + H –N – (CH2) 6 – N – H
(iii)from each functional group an element is removed so as to form a molecule of HCl and the two monomers join at the linkage .
O O H H
Cl – C – (CH2 ) 4 – C – N – (CH2) 6 – N – H + HCl
.
Polymer bond linkage
The two monomers each has six carbon chain hence the name “nylon-6,6”
The commercial name of Nylon-6,6 is Nylon It is a a tough, elastic and durable plastic. It is used to make clothes, plastic ropes and carpets.
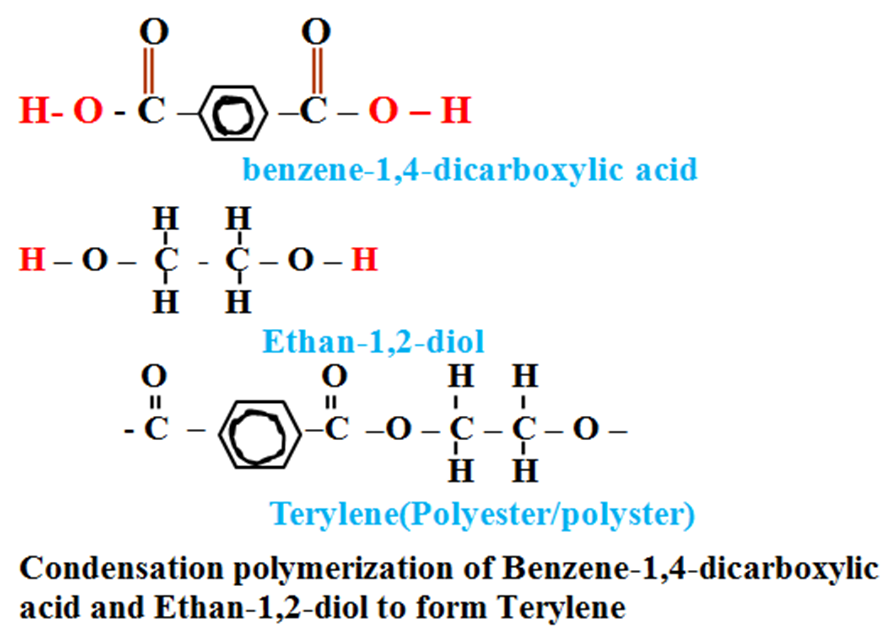
2.Formation of Terylene
Method 1: Terylene can be made from the condensation polymerization of ethan-1,2-diol with benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid.
Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid a group of homologous series with a general formula R-COOHwhere R is a ring of six carbon atom called Benzene ring .The functionalgroup is -COOH.
During the formation of Terylene:
(i)the two monomers are brought together by high pressure to reduce distance between them and realign themselves at the functional groups.
O O
H- O – C – C6H5 – C – O – H + H –O – CH2 CH2 – O – H
(iii)from each functional group an element is removed so as to form a molecule of H2O and the two monomers join at the linkage .
O O
H- O – C – C6H5 – C – O – (CH2) 6 – N – H + H 2O
.
Polymer bond linkage of terylene
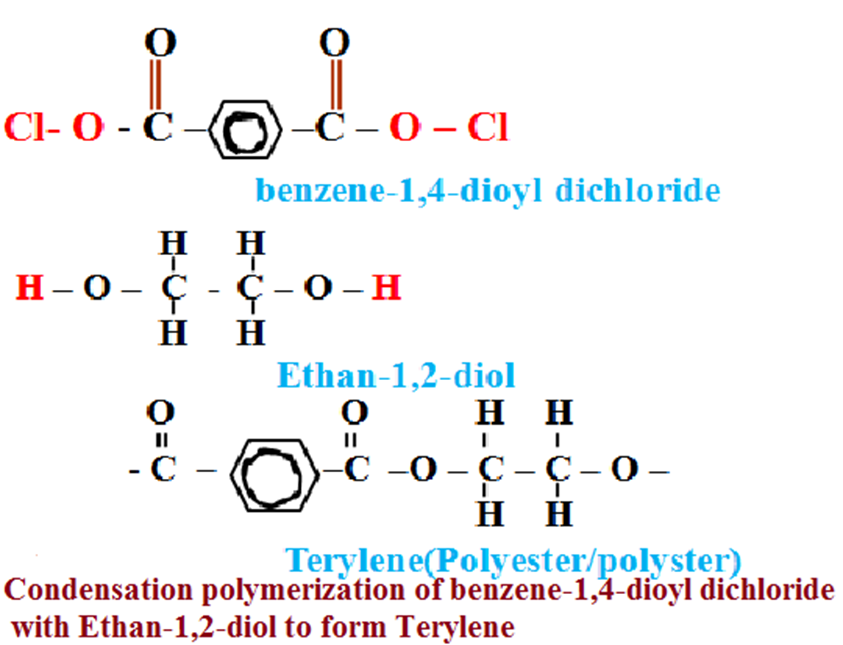
Method 2: Terylene can be made from the condensation polymerization of benzene-1,4-dioyl dichloride with ethan-1,2-diol.
Benzene-1,4-dioyl dichloride belong to a group of homologous series with a general formula R-OCland thus -OCl as the functionalgroup and R as a benzene ring.
The R-OCl is formed when the “OH” in R-OOH is replaced by Cl/chlorine/Halogen
During the formation of Terylene
(i)the two monomers are brought together by high pressure to reduce distance between them and realign themselves at the functional groups.
O O
Cl – C – C5H5 – C – Cl + H –O – CH2 CH2 – O – H
(iii)from each functional group an element is removed so as to form a molecule of HCl and the two monomers join at the linkage .
O O
Cl – C – C5H5 – C – O – CH2 CH2 – O – H + HCl
.
Polymer bond linkage of terylene
The commercial name of terylene is Polyester /polyster It is a a tough, elastic and durable plastic. It is used to make clothes, plastic ropes and sails and plastic model kits.
