CHECK THE ANSWERS AFTER THE QUESTIONS
1. i) Define the term land pollution
ii) Explain four causes of land pollution
iii) Explain four effects of land pollution
2. a ) Reasons why National parks are located in marginal areas.
(b) Explain three ways in which water pollution affect wildlife
(c) (i) State three causes of floods in Kenya
(ii) Explain two methods used to control flooding in Kenya
(d) State six reasons why it is important to manage and conserve environment
3. (a) Give three causes of sound pollution
(b) State two major health effects caused by sound pollution
4. (a) Apart from flooding, name three other environmental hazards experienced in Kenya
(b) (i) Name two rivers to the west of Rift valley which causes large scale flooding
(ii) Explain four problems caused by floods
(c) Explain three effects of land pollution on the environment
(d) (i) State three ways through which land pollution can be controlled (ii) Give three effects of wind as an environmental hazard in Kenya
5. Use the map of Kenya below to answer question (a)
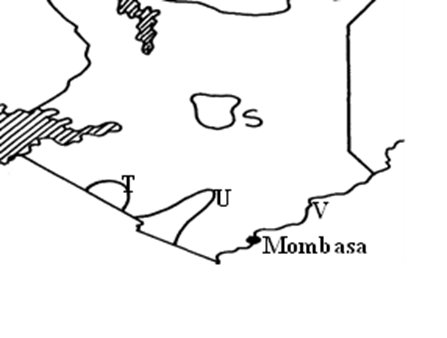
(a) (i) Name the wildlife conservation areas marked S, T, and U
(ii) Identify the Marine National Park marked V
(b) (i) Apart from Marine and Wildlife name three other tourist attractions along the coastal
strip of Kenya
(ii) Give four reasons for wildlife conservation in Kenya
(iii) Explain four problems facing wildlife conservation in Kenya
6. (a) Give three reasons why it was necessary to conduct a pre-visit before the actual study (3mks)
(b) State three measures that they could propose to be taken to promote domestic tourism
in Kenya (3mks)
7. (a) Apart from floods, name any other environmental hazard experienced in Kenya
(b) State two causes of desertification
(c) Give two reasons why it is necessary for Kenya to conserve her environment
8. (a) Differentiate between management and conservation of the environment.
(b) Give four reasons why we need to manage and conserve the environment.
(c) Explain four effects of air pollution on the environment.
(d) (i)Give five measures that can be put in place to combat pollution.
(ii) Identity three human characteristics you may learn from the garbage;
9. (a) Define the term pollution as used in Geography.
(b) Dither their air pollution name three forms of pollution.
10. Apart from desertification, name two other environmental hazards experienced in Kenya
ANSWERS FOR MANAGEMENT AND CONSERVATION OF THE ENVIRONMENT
1 i) Land pollution Is the contamination of the land through improper disposal of waste
ii) – Spraying of crops with chemicals contaminates the land by affecting soil
composition
– Careless dumping of domestic waste and industrial waste contaminates land
– Burning of vegetation during land
– Preparation leads to death of micro- organisms making the land unsuitable for plants to survive
– Poor disposal of non- biodegradable material like plastic and polythene papers contaminates the land
iii) – Bad Odour leading to air pollution
– Accumulation of domestic and industrial wastes on the road side blocks the drainage system
– Mounds of wastes are a breeding ground for flies, mosquitoes and rodents which can
cause outbreak of diseases
– Injuries can result from broken bottles, rusted metals and iron
2. a) ii) – Its best economic use of land because Agriculture does not do well in those areas.
– Population is low and this reduces conflicts between man and animals.
– It requires extensive land that is only available in those areas.
– It reduces the conflict of resettling people.
b) – Polluted water cause death of aquatic animals.
– High concentration of organic and inorganic nutrients in water causes electrification
in lakes.
– Water pollution causes diseases to animals
c i) – When a river contains excess waters which it cannot hold within its channel.
– When the level of the sea or lake rises due to increased rainfall.
– Exceptional heavy rainfall like El nino results in excess water on land.
– When a dam built across a valley breaks, the water in the reservoir floods lower land
down stream.
– When massive earthquake occurs on the seabed – causes tsunami which causes
flooding in coastal areas.
c ii) – Construction of dykes, dams and levees. These can be constructed across rivers to
control the speed of water/amount of water flowing downstream.
– Reforestation on slopes and river banks reduces surface run off and erosion / increases
the rate of water infiltration in the ground.
– Improving and diverting river channels.
– Shallow rivers can be dredged to increase their depth. /Rivers with meanders ca be
straightened to enable water flow swiftly./ Tributaries can be drenched to reduce the
volume of water getting into the main river.
d) – To sustain human life.
– To protect endangered species.
– For sustainable utilization of resources.
– For aesthetic value.
– For future generations/posterity.
– To curb global warming.
3. a) – Hooting and roaring off engines by motor vehicles
– Reverting of machines in rolling mills and welding
– Banging of metal containers by Jua kali artisans
– High pitched music played in vehicles, dance and disco halls, homes and religious
gathering
– Aircrafts as they take off or land in airports
– Blasts from mines and celebrations e.g. Dawali
b) – Rise in blood pressure and tension of muscles/physical stress
– Affects the nervous system causing neurosis and irritation
– Damage of eardrums causing deafness
a) – Desertification
– Lightning
– Windstorms
– Pest and diseases
– Pollution
4. (a) – Earth quakes
b i) – Nyando
– Nzoia
– Yala
– Kuja/Gucha
ii) – the stagnant water becomes breeding ground for vectors that cause water related
diseases.
– Floods cause loss of property/lives
– Floods cause soil water logging which lower crop production
– Floods wash away crops leading to food shortages/famine
– Floods wash away bridges/roads/telephone lines/air field disrupting transport and
communication
– People are dispatched by floods are made homeless
c)- the garbage man result to foul smell/air pollution which is hazardous to human health
– when it rains the dumped waste garbage is washed to rivers causing water pollution
– garbage can be a breeding ground for rodents /flies/cockroaches which can cause
diseases outbreak e.g. plague
– accumulation of garbage leads to blockage of roads/drainage systems
– garbage heaps are eye sore as they made the environment ugly
d i) – burning waste materials
– digging pits throwing rubbish
– minimizing use of harmful chemicals/use of organic manure
– creating public awareness on the dangers of land pollution and how to control it
– recycling of waste materials
– government logislation against dumping
– setting up proper garbage collections programmes
ii) – strong winds destroy trees
– wind blow off roofs of houses
– winds cause strong see storms and lead to boats capsizing/communication lines are
destroyed/destruction of transport lines
– winds cause soil erosion
– winds spread air-borne disease
– winds spread bush fires
5. a i) S – Mt. Kenya Nationa Park
T- Amboseli Naitonal Park
U – Tsavo National Park
ii) Malindi Marine park
bi) – Pie-historic sites e.g. Gedi ruins
- Sandy beaches
- Caves, cliffs/coral reefs (coastal landforms)
- Warm, sunny weather
- People’s culture
ii) – Ensures maximum use of less productive land e.g. arid and semi-arid regions
- Source of foreign exchange through payment of fees at entry points/gates to parks/reserves
- Creation of employment opportunities as guides in parks, lodges e.t.c.
- Protection and conservation of endangered species e.g. rhinos, elephants e.t.c. for future generation/prosperity
- Enhances research/promotes education in plants and animal species
- For aesthetic purpose/recreation
- Has stimulated the need to build roads and airstrips connecting parks with urban areas/opening up remote areas.
- Promoted diversification of the economy from over-relying on agriculture to tourism
iii) – Illegal hunting/poaching of wildlife/game leads to extinction of some animal species
- Overstocking of wild animals leading to destruction of the natural environment/overgrazing
- Frequent drought leading to loss of animals through starvation and death
- Human wildlife conflict leading to destruction of crops and death of people, through high costs of compensation
- Inadequate capital limits governemnt conservation effort especially to construct game parks
- Pollution of the environment leading to loss of wildlife
- Fire outbreaks which destroy vegetations/animals
- Pests and diseases e.g feline immune deficiency virus that threatens lion population
6. (a) – To get in contact with the park management and seek permission for the visit
-To identify and engage the services of a tour guide
– To identify the methods to be used in data collection
– To formulate the relevant objectives and hypotheses
-To assemble the appropriate equipment for the study
– To help in estimating the cost of the study
– To prepare an appropriate work schedule
– To determine the appropriate routes to be followed
– To identify possible problems that may be experienced and ways of avoiding them
(b) – Offering incentives like reduced tariff rates by hotels during the low season for local people
– Lowering the entrance fees for local people into national parks and game reserves
– Encouraging employers to offer incentive holidays to their employees
– Promote domestic tourism through the media
– Encourage young people to tour their country by establishing wildlife clubs in schools
7. a) – Desertification.
- Lightning
- Wind storm
- Pests and diseases
- Pollution
b) – Deforestation
- Poor agricultural activities e.g overgrazing, monoculture, overcroping etc
- Increase in population.
- Bush fire
- Global warming
c) – To ensure proper utilization of resources without damage.
- To sustain human life since it wholly dependent on the resources for survivial.
- To preserve the asthetic value such as landscape and vegetation of her environment.
- To protect the endangered species of plants and animals.
8. a) – Management of environment refer to the effective planning and control of the
processes that could harm the environment while.
– Conservation of environment refers to the protection and presentation of natural
resources from destruction wastage or loss.
b) – For sustenance of human life.
- To protect endangered species.
- For aesthetic value.
- To interlize natural resources
- For future generations.
- To preserve cultural heritage.
c) – Gases from factories corrode roofs of houses.
- Some poisonous gases lead to earth to form acid rain which is harmful to life.
- Smog and smoke reduce visibility which way lead to road/air accidents.
d) (i) – Control soil erosion
- Regular inspection of factories
- Setting up recycling plants.
- Treatment of sewage.
- Managing garbage collect and disposal well.
- Use of unleaded fuel
- Proper legislation.
(ii ) – Age of the population
- Social – economic status of the population.
- Culture of the people.
9. a)- Pollution is the contamination of the environment with substances which are harmful or – poisonous to human, plants and animal life.
b) – Land /Soil/Ground pollution.
- Water pollution
- Noise pollution.
10. a) – Flooding
- Lightening
- Pests/diseases
- Hailstorms
- Dusts storms
- Landslides
- Pollution
- Soil erosion
- fire
