MARKING SCHEME
CHEMISTRY FORM 1
END OF TERM EXAM 3 2022
TIME: 2HRS
INSTRUCTIONS
- ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN SPACES PROVIDED
- The pH scale has a range of values ranging from 0 to 14. On the pH scale, any substance with a pH value of 7 is neutral. Classify the following substances as either strong or weak acids or bases using their PH values. (4mks)
(a) PH 8
- Weak base
(b) pH 6
- Weak acid
(c) pH1
- Strong acid
(d) pH12
- Strong base
- Grape juice is sour while aloe juice tastes bitter. What name is given to substances which taste (2mks)
(a) Sour
- Acid
(b) Bitter
- Base
- Complete the following word equation. (7mks)
(a) Acid + base …salt………… + ……Water………………
(b) Acid + ……Metal…………. salt + hydrogen gas
(c) Acid + Carbonate ………Salt…………..+ …Carbon (IV) oxide……… + water
(d) Acid + Hydrogen Carbonate salt + …Water…………………..+……Carbon (IV) Oxide
- Study the table and answer the questions that follow. (3mks)
| Solution | Indicators | ||
| Colour in A | Colour in B | Colour in C | |
| Soap | Purple | Colourless | Orange |
| Baking powder | Blue | Pink | Yellow |
| Dilute hydrochloric acid | RED | Colourless | Pink |
| Vinegar | Red | Colourless | Pink |
Identify the indicators A, B, and C
A Litmus
B Phenolphthalein
C Methyl orange
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow:
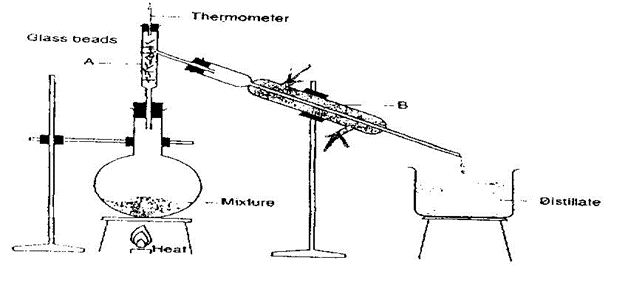
(a) Name the process of separation above. (1mk)
(b) Name the parts labeled A and B. (2mks)
A Fractionating column
B Leibig condenser6
(c) Explain the role of glass beads. (1mk)
- Increases the surface area for effective condensation.
(d) Indicate the direction of flow of water in apparatus B. (2mks)
- Matter may change from one state to another under sustain conditions. Study the illustration below and answer question that follow. (6mks)
Name process A to F
A Condensation/ Liquefaction
B Freezing/solidification
C Melting/fusion
D Evaporation/vaporisation
E Sublimation/deposition
F Sublimation
- Consider the diagram below. (3mks)
Name the parts indicated on the diagram which represent.
(i) Unburned gas zone Pale blue zone
(ii) Pale blue zone green blue zone
(iii) Green blue zone unburned gas
- State any five laboratory safety rules. (5mks)
- Never taste or eat anything in the laboratory to avoid poisoning.
- Never smell gases directs
- Label all the chemicals you are using to avoid confusion.
- Always keep flammable substances away from flames because they easily catch fire.
- If a chemical gets on your skin or in your mouth rise it immediately with a lot of clean water.
- (a) The following table contains some elements. Study them and complete the table with correct symbols. (5mks)
| Elements | Chemical symbol |
| Sulphur | S |
| Carbon | C |
| Oxygen | O |
| Hydrogen | H |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Sodium | Na |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Copper | Cu |
(b) The following table contains chemical symbols. Write down the name of the element represented by the symbol.
| Chemical symbol | Name |
| Pb | Lead |
| Fe | Iron |
| K | Potassium |
| Ag | Silver |
| Hg | Mercury |
- What is matter? (1mk)
- Is the study of the structure, properties and composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes.
- Name the three states of matter (3mks)
- The diagram below shows chromatograms for five different dyes.
(a) Name the technique used to separate the dyes. (1mk)
- Chromatography
(b) What properties are required to separate the chromatograms in a dye? (1mk)
- Different solubility/rates
- Solubility in a given solvent.
- Different densities.
(c) On the diagram above label the solvent front by using a letter H. (1mk)
(d) Which letter represent baseline on the diagram. (1mk)
- G
(e) Which dye is insoluble? (1mk)
- B
(f) Which dye is pure? Explain (1mk)
- C and A they have only one chromatogram.
(g) Which chromatogram is most soluble? (2mks)
- E it moves furthest.
- Give five differences between non-permanent (physical) and permanent (OS chemical). (5mks)
(i) Non- permanent
- No new substance is formed
- Reversible
- No change in mass
- No energy charge
- Change is temporary or physical.
(ii) Permanent
- New substance
- Irreversible
- Change in mass
- Energy charge
- Chemical change
- (a) Study the following table and classify the changes as non-permanent (physical) or permanent (chemical) after the action of heat. (2mks)
| Substance | Original colour before heating | Colour of residue after heating | Type of change | |
| 1 | Copper ii Sulphate | Blue crystals | White powder (solid) | Chemical |
| 2 | Potassium | Purple | Black solid | Chemical |
| 3 | Zinc oxide | White (oxide) | Yellow when hot and white when cold | Physical or non-permanent |
| 4 | Iodine | Black solid | Purple vapour when hot and black solid when cold | Physical or permanent |
When water was added to the white Copper II Sulphate it turned to blue, explain the type of change. (1mk)
- Temporal chemical change.
(i) What name is given to the blue copper II Sulphate? (1mk)
- Hydrous/hydrated
(ii) White Copper II Sulphate. (1mk)
- Anhydrous/an hydrated
- What is the confirmatory test for the presence of pure water? (1mk)
- Pure water boils at 1000C at sea level.
- Define the following
(i) Mixture (1mk)
- The elements (substances) in the mixture retains their chemical properties.
- Two or more elements/substances physically combined and separated by physical means.
(ii) Compound (1mk)
- A pure substances made up of two or more elements chemically combined.
(iii) Write a word equation when iron metal is heated together with Sulphur element to form iron II Sulphide. (1mk)
- Iron + Sulphur iron II Sulphide.
- Name any four apparatus used to measure accurate volumes in the laboratory. (4mks)
- Volumetric flask
- Burette
- Pipette
- Measuring cylinder
- Describe how you would separate a mixture of Iodine, salt and sand. (5mks)
- Heat to sublime Iodine.
- Add water to dissolve salt.
- Filter to obtain sand and salt solution.
- Evaporate to obtain salt.
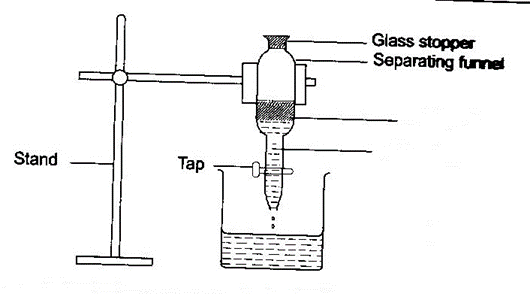
- Draw a well labeled diagram, how a mixture of oil and water can be separated. (4mks)