FIND QUESTIONS HERE
1. a) Capture –recapture method;
b) Calculate the population of grasshoppers using the above data
FM x SC = 36 x 45; = 405;
MR = 4
2. a) Help to breakdown dead organic matter hence reducing bulk; in the recycling of Nutrients;
b) Regulate the predator – prey population;
3. a) Grass___________ grasshoppers ____________ birds;
b) Not all the energy is transferred from one trophic level to another; some is lost as heat, some
is used up during metabolism and some is lost when organisms die and decay;
4. Autecology is the study of population / study of members of a species;
Biomass is the quantity of matter of a given type of organisms at a given trophic level;
Or the dry weight of an organism;
5. – Availability / adequate food supply ;
– Absence of predations ;
– Absence of disease; (mark the first two pts
6. (a) Habitat – physical location with asset of condition where an organism lives; while
niche is the exact place where an organism occupy and its role in the habitat;
(b) Producers have a greater biomass than primary consumers since they start the food chain.
Inter-trophic energy losses occur in form of heat;
(c) It is non-toxic; It’s organism specific;
7. Reduce oxygen supply and hence suffocation and death of plants and animals, clog respiratory surfaces (gills and stomata) leading to death;
8. (a) Food web;
(b) Three;
(c) Sun
9. a) Microscopic plants- mosquito larvae- small fish- large fish- crocodiles
b) Large fish;
10. a) Owl is nocturnal , white mice are easily seen and predated on, black mice camouflaged/ not
easily predated on;
b) (Theory of) Natural selection;
11. a) Capture recapture method
b) i) P = FM x SC
MR
= 725 + 974;
139
= 5080;
Where FM – First marked
SC – Second recapture
MR – Marked recapture
P – Population
ii) – No fish moves in or out of the area between counts ;
– The marked fish mix freely with other fish populations;
– Marking does not expose the fish to predation ; – No variation in population size ;
12. D A C B
(b) – Correct label;
– A,B same size;
– C-largest;
– D- smallest;
13. – Protects delicate internal parts from mage;
– prevents excess loss of water (desiccating);
– provides surfaces for attachment of body muscles / organs;
14. a) Grass Grasshopper Guinea Fowl;
Grass Termites Guinea Fowl;
b) – Leopards will decrease;
– Gazelles will also decrease;
c) Grass;
15. Population — all members of one species occupying a particular habitat at a given time;
Community — all organisms belonging to different species that interact in the same habitat;
16. – lay down two ropes parallel to each other a meter apart; count the number of shrubs between
the two ropes at marked points; and record the number; repeat the process several times;
Obtain average number; calculate area of the belt transect.
17. a) Population = FM X SC
Mr
P = 10 X 50 = 500;
4 4
= 125;
b) No entry or exit of fish;
Tags did not influence the general behavior of fish
18. – they decompose organisms; aid in nutrient circulation
19. i) Accumulation of CO2 in the atom
ii) Increase in environmental temperature
- Eratic weather changes
20. – Enzymes amylase digests starch to maltose
– Mucus lubricates food
21. Due to (stiff) competition for available resources which leads to elimination/exclusion;
22. a)feeding level;
b)quaternary consumer;
c)sun/source of energy;
23. Adaptive radiation/divergent evolution;
24. i)crab pop= number marked in 1st catch x total no. in 2nd catch
Number marked(recaptured)in second catch.
= 400×360
90
=1600;
ii) Capture mark release recapture/
Capture-recapture /capture release /recapture;
25. (a) Suck small crawling insects (from tree trunks):
(b) Catching (flying) insects in grass:
26. (a) Used for the collection of flying specimens such as butterflies;
(b) Used for sucking small insects from barks of trees and under stones; p
(c) Used for trapping crawling insects such as termites; p
27. 1. Competition; p
2. Emigration; p
3. Predation; p 4. Parasitism;
28. (a) Biotic and abiotic factors (2x ½ =1mk)
(b) – Feacal analysis
– Type of dentition type of beak (2 x1=2mks)
29. X – denitrifying bacteria/
Y – Animals/ herbivores; accept primary consumers
Z – Nitrogen fixing bacteria (in soil) accept Azotobacter
30. a) Check graph
- Labelling axes;;
- Scale
- Plotting;
- Joining (smooth contineas);
- Identifying the graph;
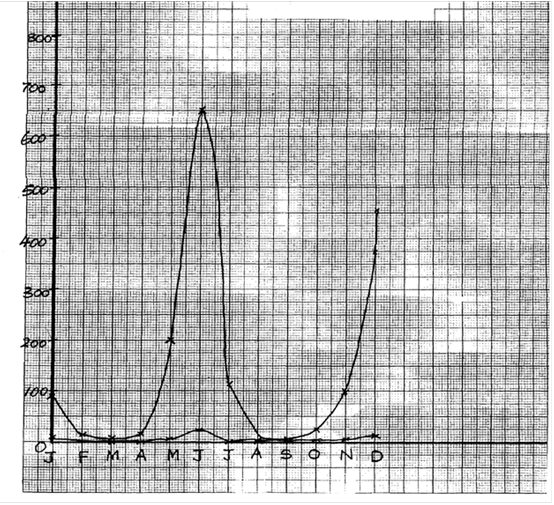
b) i) The population of locusts increase with increase in that the amount of rainfall;
ii) – Increased amount of food;
- Improve breeding conditions;
c) – The population of both decreases
– Less food availability for locusts and hence crows;
d) i) Quadrat method;
ii) total counts
e) i) locusts ____ primary consumers;
Crows ______ secondary consumers;
ii) Grass ____ Locusts ________ crows;
f) – Grass would increase;
– Crows would reduce;
g) Wild animals are browzers hence obtain food while cows are grazers hence lack grass
h) Biomass is the total dry weight of organisms at a particular trophic level;
31. (a) (i) Antelope A;
(ii) Reason- Rate of multiplication /reproduction is higher in species A than B;
(b) (i) Sigmoid curve /ogive/s-shaped curve;
Accept any one correct
(ii) PQ- Lag phase /slow growth phase; QR- Exponential/log / rapid growth phase;
RS – Deceleration phase ST- Stationary/constant growth phase;
(c) (i) Q and R
Marked with rapid population growth rate; many mature reproducing organisms/individuals/antelopes;
Absence of environmental resistance;
(ii) S and T – Growth rate stagnant/birth rate equals to death rate; the ecosystem has attained
its carrying capacity/environmental resistance (density dependent) have set-in;
(d) (i) Interspecific;
(ii) Thin and tall; yellow/pale green; low yield
(e) By occupying different (ecological) niches;
(f) Move swiftly to escape predators; camouflage to avoid noticed by predators; Eyes on the
side of the head to give them a wide field of view enabling them to keep track of their enemies;
(g) Capture –recapture method,; direct count,
Aerial photography
32. Water- The availability of adequate amounts of water lead to plant growth which
provides food for animals. In aquatic environment, wateris a medium in which gametes are released thus lead to continuity in procreation.
Temperature- Influences the rate of enzyme catalyzed reactions. Therefore, it exerts an influence on almost all activities of plants and animals such as respiration, photosynthesis, growth, transport e.t.c.
Light-Is necessary in plants for photosynthesis as it influences flowering of a wide variety
of plants, affecting opening and closing of stomata, affect the rate of transpiration.
Salinity- Is the salt content of eater. It varies in aquatic habitat. Fresh water organisms suffer the
risk of loosing water.
Humidity – Determines the amount of water loss from a bodies animals and organs of plants;
high humidity means less evaporation; and low humidity means high rate of
evaporation and transpirations;
pH – It determines if water habitat is acidic or alkaline; PH has a great influence on
physiological function of organisms affects enzyme concern reactions since
enzymes operate within a narrow pH ranges
Wind– Wind came physical damage to plants; increase rate of transpiration as air blows
away; causes migration of insects; wind having gases may acid rain in a region;
wind is an agent of pollination and dispersal;
33. (a) Grasses Caterpillar Frogs Snakes Hawk Grasses Squirrel Hunting dogs Hawk Vulture Grasses Elephant Vultures
Grasses Caterpillar Snake Hawk
(b) Pyramid of numbers.
(i)
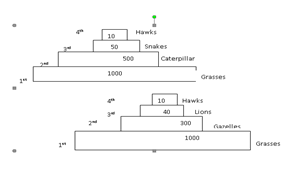
– Increase in number of gazelles and squirrels due to reduced predation leading to
increased pressure upon the grass;
(d) During transfer of energy at each feeding level, some amount of energy in form of heat is
lost only about 10% would be transferred from the grains to steers and out of the 10 %
about 1 kg would be transferred to man. The rest would be lost as heat or ingestible
material.
34. a) i) Slugs; mice;/ Amphids/ caterpillar
ii) Primary consumers;
b) i) plants _________ mice _______ snakes __________ Hawks;
Plants ________ Caterpillar ________ insectivorous birds _______ hawks
c) Plants ;_________ directly obtain energy from the sun
Hawks – Loss of energy in form of heat; through process of respiratal/ defaecation/ excretion
35. a) A lot of food causes population increase due to high rate of reproduction and immigration resulting in completion for food/ death/ emigration; reducing population; little food leads to competition; leading to emigration/ death; reducing population
b) Energy from the sun is trapped by green plants; during photosynthesis; producing chemical energy/ carbohydrates/ food
Green plants are producers/ 1st trophic level; Green plants are eaten by herbivores which are primary consumers/ occupy the second trophic level, when plants dies and animals die organisms die; saprophytic fungi/ bacteria/ micro organisms feed on them; thus decomposing them into smaller/ simpler substances/ they are decomposers/ detritivores; At all levels some energy is lost; through respiration
36. a) A- Ovary
B- Oviduct/ fallopian tube
C- Uterus/ uterine wall
D- Cervix
b) Produce ova
Produce femme hormones/ Estrogen and progesterone
c) – Highly vascularized to supply nutrients to foetus/ drain away excretory wastes
– Inner wall lined with Endometrium for implantation of fertilized egg/ zygote
– Muscular for peristalisis to expel menses during menstruation/ parturition
– Great capacity to expand during gestation to accommodate developing foetus
d) -copulation/ Achieve orgasm in Human male followed by ejaculation
– birth canal
37. a) use the capture -recapture method; capture the grass hoppers; count; and mark using
permanent ink; record; releases; and allow time(1-24hrs);recapture and count the marked and unmarked;
Total population is equal to the number marked and unmarked grasshoppers in the second sample X number of marked grasshoppers in the first sample ; divided by number of grasshoppers marked in the second sample that were recaptured;
Acc P= FMxSC
MR
where FM-1st captured
SC-2nd capture(marked and unmarked
MR-marked recaptured
(rej. ½ mark i.e. 10/2=5) acc specified distance apart e.g. 3m apart
b. run two ropes parallel to each other a meter apart; counts of shrub are made between the two ropes at marked points/whole belt (and recorded);report the process severally(at least 3 times);calculate shrub area of the belt transect; calculate shrub population for whole area;
Rej all shrubs counted
NB shrub pop=average shrubs per transect x total area of grassland
Average area of belt transect (max 3)
38. (a) (i) Phytoplanktons:
(ii) Hawk; and water snake:
(b) – Decrease in phytoplanktons:
– Increase in population of small fish:
(c) Hawk;- Top predator amount of energy decreases in successive trophic level/energy is lost
through respiration; undigested/unconverted food:
(d) Residue is poisonous to man;
-Kill non- targeted organism / Beneficial organisms:
-Remains for along time in the ecosystem / pollutes environment:
(e) (i) Causes decomposition/Recycling of nutrients:
(ii) Root nodules: have bacterial / Rhizobium sp: to convert free nitrogen: into nitrates in the
soil;
(f) Capture – recapture: capture release recaptures:
(g) Manufacture food: (OWTTE) to be used by themselves: and all other organisms in the
ecosystem ( awls)
39. Broad/ wide lamina: to Provide a large surface area to trap maximum sunlight or
photosynthesis;
– Thin lamina; to reduce the distance covered b\ light and carbon (iv) oxide: to reach the
photosynthetic cells/ palisade cells;
– Cuticle; is transparent to allow light reach photosynthetic cells:
– Waterproof climatic cuticle: to reduce water loss/Transpiration:
– Numerous stomata: efficient gaseous exchange: palisade (mesophyll) cells: have numerous
chloroplasts: for maximum photosynthesis: spongy mesophyll cells: are irregular in shape
creating large air spaces between: for efficient /free circulating air; Lear veins; have x 1cm 1r
transport of water and mineral salts: and phloem for transport of manufactured food;
– Leaf mosaic: to maximum trapping of sunlight for photosynthesis:
– Guard cells: to control opening and closing stomata: Guard cells have chloroplasts for
photosynthesis:
