1. a) BB;
b) AA;
2. a) Black mice are better adapted camouflage with the environment hence less are eaten by the
owls compared to the white mice which are easily seen;
b) Theory of natural selection;
3. – Heterostly – stigma located above anthers;
– Self sterility or incompatibility – pollen grain from the same plant do not germinate
– Protandry – Male parts mature before female parts;
– Protogyny – Female parts mature before male parts;
4. (a) Complete dominance is when an alliele completely surprises another intermediate fruits;
Incomplete dominance is when heterozygous organisms show an intermediate trait;
(b) Genetic recombination’s of alleles reading to variations; Independent assortment of
chromosomes;
Random fusion of gametes; mutations;
Environment (may either enhance or suppress expression of a gene);
5. (a) C-A – G – U – C _ A ;
(b) – Stones genetic information (in a coded form);
– enables transfer of genetic information unchanged to daughter cells through replication);
– Translates genetic information into characteristic of an organism 9thorugh protein synthesis);
6. Ability to pollinate; response to stimuli (tactic) nastic or tropics); Ability to exploit localized nutrients an ability to photosynthesize; Ability to disperse seeds/fruits, propagation;
7. (a) Glucose;
(b) The person was a sufferer of diabetes mellitus;
(c) Pancrease;
8. Continuous variation shows gradation in characteristic with intermediate; discontinuous shows distinct characteristics between organisms with no intermediate groupings;
9. -mutation;
-intermixing of genes already in the population through sexual reproduction recombination;
-crossing over during prophase of meosis I
-interdependent assortment of chromosomes, during metaphase of meosis I
10. i) Substitution;
ii) Deletion;
iii) Inversion;
11. i) C G G A T C T A G T G;
ii) C G G A U C U A G U G;
12. a) Continuous ;
b) Nutrition/ environment; genes;
13. a) Father XHY ;
Mother XHXh ;
b) i) Genes found in the same chromosome and usually transmitted together;
ii) Across to determine an unknown genotype involving use of a recessive parent;
14. a) Colour blindness; haemophilia;
Sickle cell anaemia;
b) Part of X chromosome has homologous portion on the Y chromosome therefore if the X has
the recessive trait, it will show on the male phenotype ;
c) The son inherits the X chromosome from the mother while the daughter inherits the
X chromosome from the father;
15. (a) Inversion ;
- ustard gas;
- ionizing radiation;
- gamma rays;
- X- rays ;
16. (a) Ribonuclei acid /RNA
– Because it has uracil / presence of uracil;
17. (a) Due to co-dominance /partial dominance/incomplete dominance/(Acc. equal dominance)
(b) Red: 2Pink : white – 1: 2:1 (Acc. 1RR: 2RW: 1WW) mark as a whole;
(c) Why women should drink extra milk;
(i) Bore formation for infants ;
(ii) pressure on bladder by the enlarging uterus;
18. a) Genes which are located on the sex- chromosomes and therefore are transmitted along with
them
Example Haemophilia; colour blindness;
b) Where more than two genes control a particular characteristic/ trait;
Example ABO blood group system;
19. a) Parental Genotype Rr, Rr ;
b) Red: white;
119/41; 41/41;
2.90: 1
3: 1;
20. (i) Y – Chromosome-hairy pinna, pre-mature boldness; ; (any one)
(ii) X – Chromosome- haemophilia (bleeders disease); colour blindness; (any one)
21. The Gene that determine the growth of long hair on pinna is sex linked and an Y-chromosomes; V hence can only be inherited by males as a single gene and it expresses itself out phenotypically
22. Due to crossing over: that results in exchange of genetic materials between homologous
chromosomes;
23. (a) Co dominance/ incomplete dominance:
(b) 1 Red flowered; 2 pink flowered; I white flowered: for ratio for phenotype)
24. (a) Albinism;
(b) Makes skin supple;
– Kills bacteria/ a mild antiseptic;
25. – Change in base sequence of the DNA; p 1.
26. (i) Sudden and spontaneous change in structure of chromosome and DNA which is inherited
(ii) Chemical ionizing radiations, Uv light, extreme temperature or some virus
27. (a) GCCTATG – DNA
GCCUAUG- MRNA
(b) Ribosome;
28. a) Parental phenotype Pink flight feathers X White flight feathers
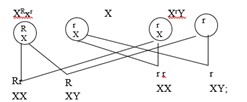
Parental genotype XRxr X XrY
Parental gametes
Fusion
F1 genotypes
b) incomplete;
c) i) Ribonucleic acid;
ii) has uracil base;
ii) – 3;
- There are three codons;
29. A – XhY;
B – XHY;
F – XHXh;
XH Xh; X Xh;Y;
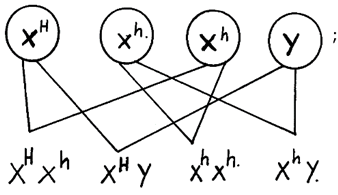
(c) Albinism; sickle cell anaemia; colour blindness; chondrodystrophic dwarfism;
30. (i) Father Mother
XHY XHYH
Since father cannot have the recessive gene ad fail to be affected. The mother must be a carrier
on her second X chromosome for a male son to be haemophiliac.
(ii) Parental phenotypes mother carrier, father normal
Parental genotypes XHXh XHY
31. a) the two genes that control flower colour ,that is the gene for red flowers and the
one for white are codominate; b) F₁ phenotype pink flowers pink flowers
F₁ genotype RW X RW ;
Gameter R W R W ;
Fussion
F₂ genotypes RR RW RW WW ;
F₂ phenotypes red
Flowered pink white flowered ;
Flowered
c)genotypic ratio= 1RR:2RW:1WW/RR:RW:WW=1:2:1 ;
Phenotypic ratio=1 red flowered:2 pink flowered:1white flowered ;
Notes: i) there must be cross on genotype
ii) gameter should be circled
d) recessive gene expressed it self only underlined homozygous condition while dominant gene expresses it self in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions;
32. (a) (i) Male and female flowers are separate hence cross pollination is made possible.
(ii) 1 Yellow : 3 Purple
Rej.: 15 yellow : 45 Purple

| F1 genotype |
(b) Let letter T represents purple maize grai
| P1 |
Let letter t represent yellow maize grain
| Parental phenotype: Purple Yellow Genotype: TT x tt Gametes: | |||
(c) Gene for purple grain;
(d) (i) Finger prints are used to identify criminals; (ii) Blood groups are used to settle parental disputes
Parental gametes
Fusion;
F1 offspring;
c) All Rhesus positive/ all RhDRhd;
(d) None
35. – By keeping their mouth open/panting; to lose heat over surface area of the tongue by evaporation;
-Basking; to gain heat by conduction;
– Shivering; to generate heat through increased metabolism;
– Physical activity (e.g. running); to generate heat through metabolism;
– Hibernation; to increase metabolism;
– Putting on warm clothes when it is cold; to retain the heat energy;
– Reduction of physical activity; to reduce the metabolic rate;
– Migratory behaviour to cooler environment; to reduce the body temperature;
– Moving into water when it is hot; to cool the body;
– Staying around fire place; to gain heat by convection;
– Taking hot drinks; to warm the body;
36. a) Parental genotypes
i) Woman/ OX – AO
ii) Man/ O – BO
b
| A | O | |
| B | AB | BO |
| O | AO | OO |
c) Cases of disputed paternity settlement
– Determining compatible blood groups in blood transfusion
d) i) Corresponding complementary DNA strand GAA;
ii) Corresponding RNA CUU
iii) Nitrates/ sulphites/ hydroquinone/ gamma/ beta/ alpha/ x-rays/ UV light/ hydrogen peroxide
37. let R rep. gene for Red flowers
W.rep gene for white flowers
a) parental phenotype Pink flowered Pink flowerd
genotype gametes
;
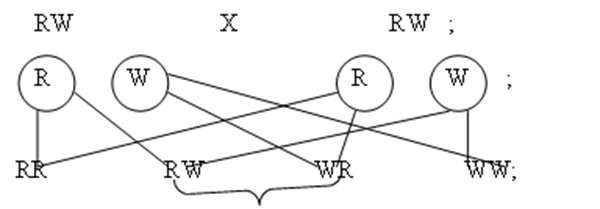
red pink white
b) phenotypic ratio 1Red:2Pink:1White;
genotypic ratio: 1RR:2RW:1WW;
c) 2 x 480;=240

Fl generation Award for punnet Square and genotypes
(b) (i) IBB : 2Bb: lbb
(1 mark for ratio, 1 mark Par genotype)
(ii) 3 B lack: I brown
(iii) 24;
39. (a) Homologous structures:
Structures of common embryonic origin modified to perform different functions;
Example: Eye structure in man and octopus/ wings in birds and insects (I mark)
Analogous structures Example
(b) They undergo mutations: resulting in new forms that rcsis selection resistant to drugs;
(c ) (i) Failure of chromosomes to separate during anaphase I resulting in gametes
with an extra chromosome and others with less chromosomes: (I mark)
(ii) Downs syndrome / Klinefelters syndrome/ Turners syndrome: any I ( 1mk)
40. a) Homologous structures have a common embryonic origin but are modified to
Perform different functions; while analogous structures have different embryonic origin but are modified to perform similar functions;
b) Nictitating membrane; post anal tail; body hair;
41. a) Pentadactyl limb structure of mammals; beaks of birds; feet of birds;
b) – Missing links between fossils because some parts or whole organisms were not fossilized
– Some parts were distorted during fossilization hence may give wrong impression
of structures;
– Some structures have been destructed by geological activities;
42. Camouflage is the conceal/ element of identity of an organism by resembling the color
of the environment while mimicry is the imitation of non- living organisms to conceal identity
43. Light energy splits water molecules; into hydrogen ions and oxygen atoms;
44. (a) Caecum/ Rumen/ pauch;
(b) Closes to prevent food from moving up the oesophagus;
45. (a) – the soft bodied organisms fail to fossilize;
– Human activities interfere with fossilization;
Earth movements e.g. volcanic eruptions interfere with fossilization; (mark any first2 pts
(b) – They resembled from neck downwards;
-They walked upright;
– The shape of the skull suggested they were able to speak;
46. a i)vestigial structures are those structures that have ceased to be functional over along
period of time and hence reduced in sizes
ii)-appendix;
-caecum
-coccyx or tail/tail bone;
– Nictitating membrane/semi – lunar fold at the corner of the eye;
-ear muscles
– Body hair;
b) Disease causing organism mutates; and became resistant;
47. Struggle for existence –environmental pressure on the population in order to survive;
Survival for the fittest-advantageous variations an individual possesses to make it survive;
48. Secretion of antidiuretic hormone; rearbsorption of salts at the loop of Henle;
49. -Divergent evolution refers to a situation where by organisms that are believed to have
had a common ancestral origin have homologous structures which have been modified to suit different environments;
50. a) Allows survival of organisms with better qualities / traits / characteristics; eliminates
organisms with unfavorable characteristics/ traits;
b) Divergent;
51. Evidence does not support Larmarks theory
Acquired characteristics are not inherited/;
Inherited characteristics are found in reproductive cells ;
52. (a) Vestigial structures
(i) Are those structures that have ceased to be functional over a long period of time hence
reduced in size;
(ii) Appendix/coccyx/tail/ nictitating membrane semilun fold at the corner of the
eye/caecum/ear muscles, body hairs;
(b) Disease causing micro-organisms mutate and become resistant;
53. a) The gradual emergence of complex life forms from pre-existing simple forms over along
period of time ;
b) Nature selects those organisms with structures that are well adapted to survival in
the environment. These structures are passed to their offspring; organisms with structures
that are poorly adapted perish ;
54. The insecticide kills most of the insects when introduced; those that survive; give rise to a new
generation of flies that are resistant to insecticide.
55. – Most organisms especially soft-bodied ones do not form fossils;
– Most fossils have not yet been discovered;
– Exposed fossils are usually destroyed by physical and chemical weathering;
– Earth movements e.g. volcanicity, earthquakes, tsunami do destroy fossils;
– Most animals are prayed upon;
56. -Fossil records/paleontology ;
-Comparative anatomy/taxonomy;
-Comparative embryology;
-Geographical distribution;
-Cell biology;
-Comparative cellulogy/immunology; (award 1st three 3mks)
