1. The diagram below represents the earth on its axis. Use it to answer question (a
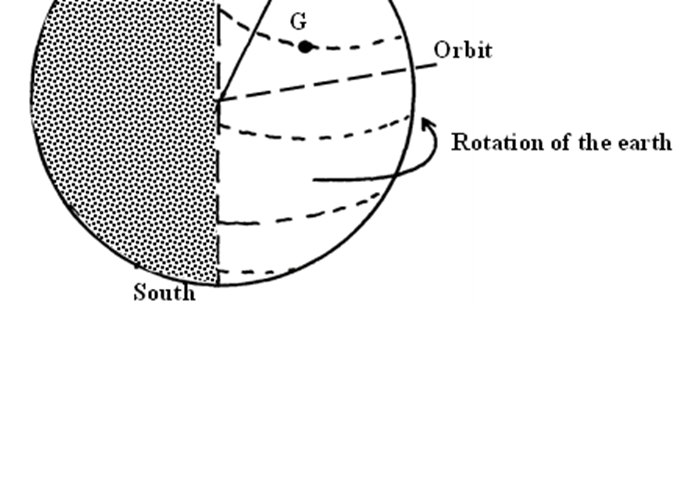
a) i) Name the latitude marked G
ii) What is the angle of inclination of the earth’s axis from its orbit
b) i) State two effects of the rotation of the earth
ii) When the local time is 2.00 p.m at longitude 45°E, what is the longitude of a place
whose local time is 10.30 a.m
c) Name two local winds experience around lake Victoria region
2. The table below represents rainfall and temperature figure for a town in Kenya .Use it to
answer the questions that follow:-
| MONTH | J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| Temp (ºC) | 27 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 27 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 26 |
| Rainfall(mm) | 25 | 38 | 99 | 140 | 277 | 439 | 277 | 69 | 142 | 201 | 71 | 25 |
a)i) calculate the annual range of temperature for the town
ii) Calculate the total annual rainfall for the town (1mk)
b) State three characteristics of the climate experience in the town
3. a) What is a solstice
b) State three effects of the revolution of the earth
4. (a) (i) Give two theories that explain the evolution of the solar system and the origin of the earth
(ii) Identify the force that causes the earth to bulge at the equator
(b) Give two reasons that support the belief that the interior of the earth is very hot
5. a) State two theories that are used to explain the origin of the earth
b) What is solar “system”?
6 a). Name two planets without natural satellites in the solar system
(b) (i) What is a time zone?
(ii) Give the reason why the International Date Line is significant. (2mks)
(c) State any two characteristics of Latitudes.
7. (a) What is the solar system
(b) Give three reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot
8. (a) The diagram below represents an eclipse. Use it to answer the following questions:
(i) Name the type of eclipse
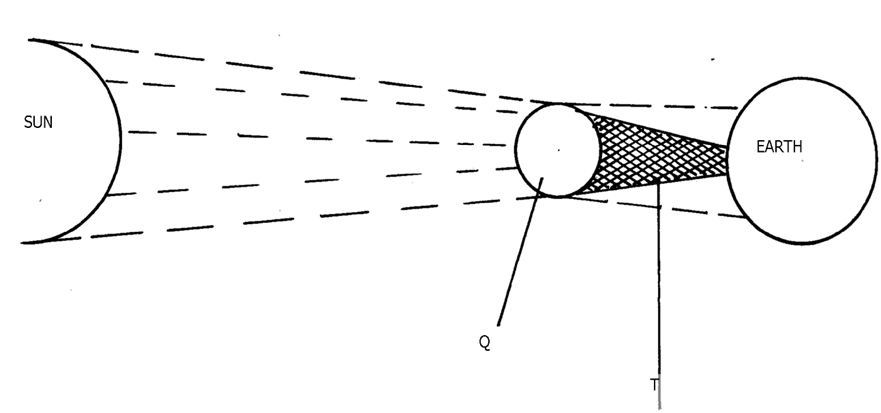
(ii) Identify the parts marked Q and T
(b) State three effects of the rotation of the earth
9. a) State three reasons why the interior of the earth is known to be very hot
b) Give two effects of the elliptical shape of the earth
10. (a) (i)What is an equinoxal date?
(ii) Name two equinoxal dates
(iii) State two changes caused by the earth’s revolution around the sun
11. The diagram below represents the internal structure of the earth. Use it to answer question (a.)
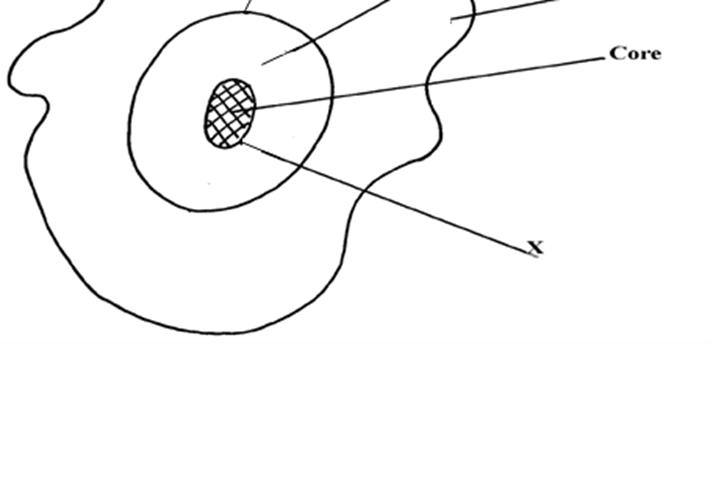
a)Name the arts named u, v and x
b) Describe the characteristics of
i)Crust ii) Core
GEOGRAPHY ANSWERS FOR THE TOPIC THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM
1. a i) i) Tropic of cancer
ii)) 66 ½ º
b i) – Causes day and night
- Causes high and low tides
- Causes deflection of winds and ocean currents
- Causes time difference between longitudes
- Causes pressure difference on the earths surface
ii) Time difference = 1400 hrs – 1030hrs
= 0330 hrs
= 3½ hrs
\Difference in longitude is
7/2 x a5 = 52.5
52.5 – 45
Longitude is 7.5W
(c) – Sea breeze
- Land breeze
- Anabatic
- Katabatia
2. a i) – 28ºC-24ºC = 4ºC
ii) – 1803mm
b) – the town experiences high temperature throughout the year (24ºC-28ºC)
- the annual range of temperature is small
- rain fall throughout the year/there is no marked dry season
- the rainfall patter has double maxima
- the wettest month is June/the driest month are December and January
- the rainfall is high i.e. 1803mm
3. a) Solstice is when the sun’s overhead position is over the tropic of caner and Capricorn
b) – Causes seasons i.e. spring, summer, autumn & winter
– Varying lengths of day and night at different times of the year
– Changes in the position of the midday sun at different times of the year
– Changes in the position of the midday sun at different times of the year
4. a i) – Passing star theory
– Nubular cloud theory
ii) Centrifugal force
b) – Layers of the overlying rocks exerts pressure hence the interior is hot
– After formation of the earth the interior cooled slowly compared to the exterior, thus the
interior still retains much of its original temperature
– Radioactivity – mineral elements with the interior react with each other thus exploding
to produce heat
5. a) – Passing star/ the big bang theory
– Nebula cloud theory
b)- The solar system is the group of heavenly bodies comprising the sun and the eight known planets which orbit the sun
6 .a) – Mercury
– Venus
b) (i) A time zone is a group of neghbouring countries that use the same standard time
ii) – On crossing this line from east to West,, a day is gained / the clock has to be
adjusted backwards by 24hours
– On crossing this line from West to East a day is lose/the clock has to be adjusted
forward by 24hours.
c) – They are circular.
– They decrease in length Northwards and Southwards
– They are measured North and South of the equator
– There values increase Northwards and Southwards
– They are parallel to each other
7. a) – It is the sun and the planets orbiting around it.
b) – The radio activity process taking place in the interior leads to a lot of energy
production.
– This keeps the temperature in the interior very hot.
– The overlying materials exert a lot of pressure to the interior resulting to higher
temperature.
– When the earth was being formed the mantle and the core cooled at a slower rate than
the crust.
– As a result the temperature in the interior are still hot.
8. a i) -Solar/eclipse of the sun
. ii) – Q-moon
– T-umbra
b) -it cause days and night
-it causes high and low tides
-it causes the deflection of winds and oceans currents
-it causes time difference between longitudes
9. a) – Cooled at a slower rate than the outer exposed part
– Due to the process of radio- activity where atoms break releasing heat
– Weight of the overlying material that exerts pressure on the core
b) – Causes seasons
– Varying lengths of day and night
10. a i) It is the date when the sun is overhead at the equator at mid day
ii) 21st march√
23rd September√
iii) – causes four seasons i.e. winter, summer, autumn and spring√
- causes varying lengths of day and night at different times of the year√
- causes changes or altitude of the mid-day sun at different times of the year√
11. a) – U-mohorovicic discontinuity
– V-the mantle/asthenosphere
– X-Gutenberg discontinuity
. b i) – it is made up of solid rocks
- composed of two layers /sial and sima/continental crust and oceanic crust
- sial is rich in silica and a aluminum
- sima is rich in silica and magnesium
- sima rocks are like plastic/more flexible
- the top layer of the sima is made of sediments and volcanic lava
- the bottom layer of sima is made up of basalt/igneous rocks
- the sima is made up of the basaltic/igneous rocks
- sima is made up of dense rocks /2.8-3.0 gm/cc
- the sial is made up of granites/sedimentary/metamorphic rocks
- the sial rocks are rigid/brittle
ii) – the core is composed of two parts i.e. inner core and outer core
- the main mineral of the outer core are iron and nickel
- the main mineral of the inner core is iron
- the inner core has a high density i.e. 16-17gm/cc than the outer core i.e. 10.5gm/cc
- the inner core is made up of a solid rock mass
- the outer core is molten
