CHECK THE ANSWERS AFTER THE QUESTIONS
1. The table below shows the population of a county in Western Europe in 1000.use it to
answer part a-c
| Age group | male | female |
| 0-4 | 450 | 455 |
| 5-9 | 447 | 449 |
| 10-14 | 448 | 450 |
| 15-19 | 454 | 458 |
| 20-24 | 480 | 472 |
| 25-29 | 630 | 632 |
| 30-34 | 635 | 639 |
| 35-39 | 642 | 671 |
| 40-44 | 670 | 638 |
| 45-49 | 636 | 568 |
| 50-54 | 562 | 641 |
| 54-59 | 633 | 639 |
| 60-64 | 631 | 634 |
| 65-69 | 451 | 452 |
| 70-74 | 470 | 468 |
| 75-79 | 460 | 459 |
| 80+ | 451 | 453 |
(a) Using a scale of 1cm to 100,000 people, draw a population pyramid from the above data
(b) State five characteristics of the above population structure as shown by the pyramid
(c) Explain four problems likely to be experienced due to the population trend in the
above country
(d) (i) What is mortality rate?
(ii) State five measures that have been taken in Kenya to reduce infant mortality in Kenya
2. a) Name two primary sources of population data
b) Explain four reasons that led to rapid population growth in Kenya in the 1980’s
c) State four reasons for increased infertility in Kenyan women today
d) Give measures taken by the government to combat child mortality
3. (a) Distinguish between population distribution and population density
(b) State any three problems associated with high population growth rate in Kenya
4 (a) (i) What is life expectancy?
(ii) Give three types of information which can be derived from a population pyramid.
(b) (i) Describe three ways in which population of Sweden differs from that of Kenya.
(ii) Explain four causes of rural-rural migration in Kenya.
(c) Explain three problems which result from the high population growth rates in the
East African countries
5. (a) Define the term secondary fertility
(b) (i) Apart from HIV/AIDS give two other causes of mortality in East Africa
(ii) State two ways in which the spread of HIV/AIDS in Kenya may slow down
economic development
c) State five problems facing regional trading blocks in Africa
6. a)i) What is dependency ratio?
ii) State three causes of a high dependency ratio in a population
b) i) Explain four factors that have led to the high population density around Lake Victoria
ii) Explain three problems associated with high population growth rate in Kenya
c) Give three reasons for the low birth rate in Sweden
7. a) What is population census
b) State three reasons why countries conduct population census
8. (a) Differentiate between immigration and emigration
(b) State three effects of rapid population increase in Kenya
9. (a) Define the term population explosion
(b) State three reasons why countries conduct population census.
(c) Give two measures the Kenya government has taken to check on high population growth.
GEOGRAPHY ANSWERS FOR TOPIC POPULATION
1a.
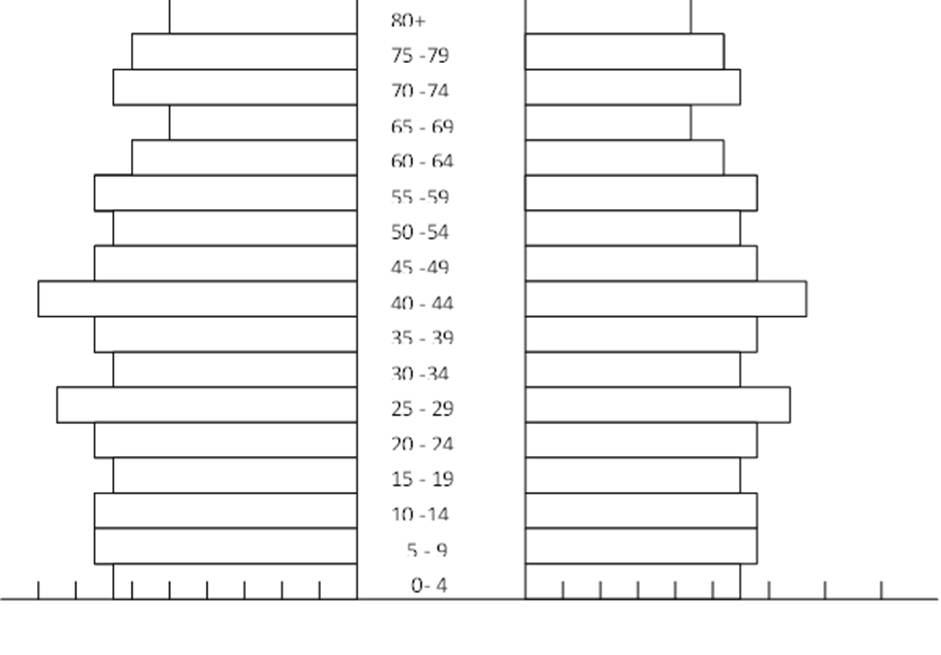
b) – Has a high life expectancy.
- Has a large working population.
- Has a low dependency ration.
- Has a low fertility rate.
- Has low death rate
c) – Inadequate manpower making labour expensive.
- Rural depopulation due to increased urbanization/leading to labour shortage.
- High old age dependency ratio due to high life expectancy.
- Under utilization of social amenities due to low birth rates.
d i) – mortality rate is the number of deaths in a population of 100 people per year.
d ii) – Improving medical facilities and immunizing children to control disease.
- Educating parent on child care during pre natal period.
- Educating parents to have planned families.
- Encouraging parents the benefits of breast feeding and balanced diet.
2. a) – Population census
– Sample surveys
b) – Improved nutrition and medical care which lowered mortality and increased
fertility hence leading births and longevity
- Increase in early marriages which increased reproductive life span hence increase
in birth rate
- Low level of family planning due to low awareness leading to large families hence rapid population growth
- Many people were still entrenched in cultural beliefs which favour having large families for security investment hence rapid population growth
c) – High literacy level and awareness on need to have small families
- Most of the women go to school and spent more time in schools or colleges thus has reduced indulgence into sex or early marriages by most women
- High abortion rate which damages the reproductive system
- Misuse of family planning gadgets and drugs which damage the reproductive system
d) – Early vaccination against polio, measles e.t.c.
- Provision of free mosquito nets to expectant mothers
- Free health care to all infants in government hospitals
- Training of traditional aids to birth delivery on modern methods of birth delivery
- Expansion of health facilities to all rural areas to increase access to health care
- Employing nutritionists to educate mothers on better nutritional practices to evade child mortality
3. a) – Population distribution is the way people are spread out on the land whereas
population density is the number of people unit area of land.
b) – A high rate of unemployment.
- High crime rate as people seek ways of supporting themselves.
- High demand for social amentities.
- The dependency ratio decreases.
- High demand for food sometimes leading to food shortages.
- Strain on natural resources and scarcity of land.
4. a i) Life expectancy is the average age to which the people of a country expect to
live/the average age at which people die
ii) – The composition by sex
- The size of population
- Proportion of dependency ratio
- Different age groups
- The proportional males to females
b i) – Population growth rate is high in Kenya and low in Sweden
- Kenya’s population has a large number of young people below 20years of age while Sweden has a high medium age population
- Death rate is high in Kenya and low in Sweden
- The fertility rate is high in Kenya and low in Sweden
ii) – Natural hazards e.g. floods force people to migrate to other areas for safety
- Pastoralists migrate from one rural areas to another in search of water and food for their livestock
- Land disputes make people move and settle elsewhere
- Pressure on land makes people to move and buy land elsewhere for settlement
- Insecurity in some areas forces people to move
- Settlement schemes attract people to settle in them
c) – Causes high dependency for social basic needs
- Leads to high rates or unemployment
- Leads to food shortages
- Leads to land fragmentation and this decreases agricultural production
- Leads to high rates of crime
5. a) It is the fertility achieved after the abstinence that is continued, when the initial
fertility was broken.
b i) – Natural calamities
– Low nutritional standards/famine /lack of food
– Conflicts
– Other epidemics/diseases.
– Inadequate/poor medical facilities
– Road carriage.
ii) – The sickness leads to absenteeism from work/reduced productivity.
– Money spent in treating the sick could be used for other economic activities.
– Deaths resulting from the disease lead to loss of economically productive
population.
– Care-takers at family level use moral time caring for the sick/orphans instead of
engaging in economic activities/high dependency ratio.
c ) – Production of similar goods
– Failure to remit annual subscriptions by members
– Different levels of industrialization
– Poverty among the population in the regions
– Poor transport and communication linkages
– Desire to [protect local industries by member countries
– Lack of common currency
6. a i) Is the number of unresourceful people between zero to fourteen years and above
sixty five years per every 1000 resourceful people
ii) – High birth rate
– Low death rate
– Scarcity of employment opportunities
(b) i) -Presence of large towns e.g. Kisumu
-High rainfall
-Fertile land
-High fertility rate
ii) – High employment rate
– Pressure on social amenities e.g. schools
– Rural- urban migration hence overcrowdings
– Too many dependants
– Pressure on land
– Food shortages
. c)- Acceptance of family planning methods
-Career advancement among Swedish women
-Decrease in infant mortality
-Advanced living standards that ensure only a small family can be catered for
7. a) Is the enumeration of the people in a given area and the compilation of demographic,
social and economic information of the population being enumerated at a given time
b) – To determine the composition of the population
– To know the trends and levels of mortality and fertility
– To plan for provision of basic facilities
– To aid in creating new administrative units
– To estimate the dependency ratio
– To know the literacy level
– To know labour supply and predict any unemployment problems
8. a) – Emigration is the movement of people out of their country and settling in another
while Immigration is the movement of people from another country into a country.
b) – Higher dependency ration leading to low investment.
– Causes land fragmentation leading to food shortage.
– Shortage of water in urban centres.
– Leads to excessive tree felling for energy requirements and to pave way for settlement
and agriculture.
– Congestion of social facilities such as schools and hospitals.
– Leads to increased unemployment.
9. a) Population explosion is the abnormal increase in people in a region, thereby
overstretching the available resources
b) – To determine the composition of the population
- To know the trends and levels of mortality and fertility
- To plan for provision of basic facilities
- To aid in making decisions regarding regarding the creation of new administrative
- To estimate dependency ratio
- To know the literacy level
- To know labour supply and predict any unemployment problems
. c) – Introduction of the national family planning programme through creation of national and
development (NCPD)
- Introduction of adult education programme to check illiteracy and teach on importance of family planning
- Creation of public awareness through mass media i.e. radios, TVs
- Encouraging men and women to opt for voluntary sterilization and discouraging early marriages through legal action and education
- Organizing family life seminars and public baraza’s
