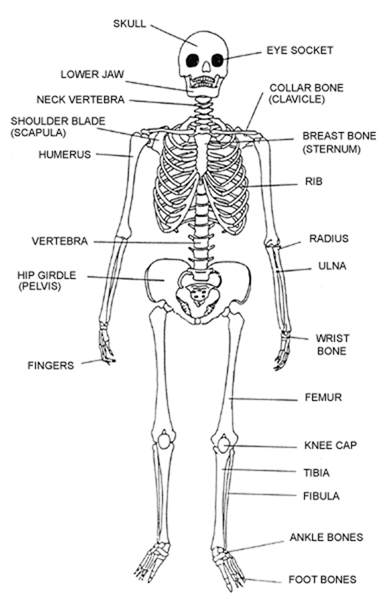
- Name the main parts of the vertebral column giving the types of bones found in each part
Axial skeleton
- forms the main axis of the body
- formed by the skull, sternum, ribs and vertebrae
Appendicular skeleton
- composed of limbs and girdles
- the forelimbs are connected to the trunk by the pectoral girdles (shoulder bones)
- hind limbs are connected to the pelvic girdle (hips)
- bones are scapular, clavicle, humerus, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula, metacarpals, carpals, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, ilium, ischium and pubis
ii) What are the vertebrae?
- bones of the vertebral column
iii) State the functions of the vertebral column
- gives flexibility
- absorbs shock
- protects spinal cord
- supports weight of body
- provide surface for muscle attachment
- between the vertebrae are soft discs which offer cushioning called interverterbral discs
iv) State the general characteristics of vertebrae
- have solid structure called centrum to support weight of body
- has transverse process lateral to centrum for muscle attachment
- neural spine is dorsal to centrum and provides surface area for muscle attachment
- neural canal a passage for spinal cord and offers protection to it
- has facets for articulation with other vertebrae
- neural arch encloses neural canal
) Name the bones of the vertebral column
– Cervical vertebra
– Thoracic vertebra
– Lumbar vertebra
– Sacral vertebra
– Caudal vertebra
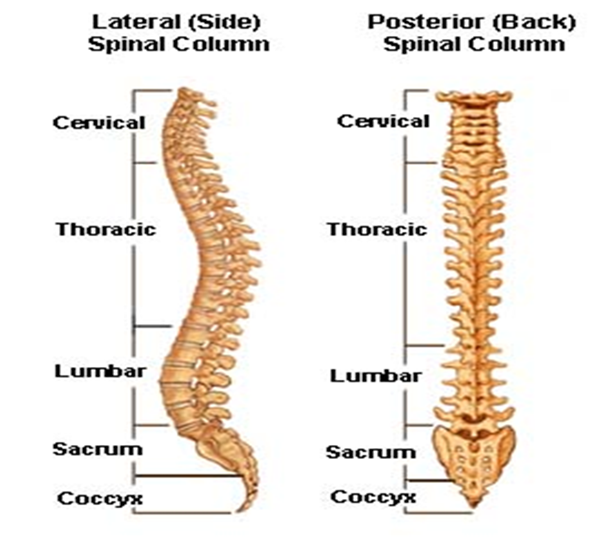
vi) Describe how the various vertebrae are adapted to their functions
| Bone | Structure | Function |
| Skull | cranium and jaw bonesmade of several bones joined togetherlarge box called cranium and smaller paired boxes for eyes, ears, nose, jawshas large hole called foramen magnum for the passage of spinal cord | attachment of jaws protect brain and other delicate parts |
| Cervical region Atlas (first cervical) | ring shapedno Centrumbroad, flat transverse processesvertebraterial canal for passage of vertebral arteryfacet for articulation of condyles of skull | protect spinal cordattachment of muscles allow nodding of head |
| Axis (second cervical) | adontoid peg projects from Centrumlarge flattened neural spinevertebrasterial canalsmall transverse process | allows head to rotateprotects spinal cordprovides surface for muscle attachment |
| Cervical (others) | short neural spinebranched transverse process for neck musclesvertebraterial canalswide neural canal | support weight of headprotect spinal cordneck muscle attachment |
| Thoracid | long backward pointing neural spinetransverse process that points sidewaysfacets for articulation of ribsnotch for spinal nerves to pass through | forms rib cagearticulation with one end of a ribprotects, spinal cordmuscle attachment |
| Lumbar | short neural spinelong transverse process pointing towards abdomenlarge Centrumextra processes e.g. prezygapophysis, hypapophysis, anapophysis, metapophysis | protect organs of abdomensupport upper part of bodyprotect spinal cordmuscle attachment |
| Sacral | fused bones to form sacrumwell developed transverse process of first vertebravertebraterial canalsshort neural spine | protects alimentary canalattachment of hip girdlesprotect spinal cordmuscle attachment |
| Rib | longflattenedattached to sternum from front | protect internal organsmuscle attachment |
vii) Describe the bones that form the appendicular skeleton
| Bone | Structure | Function |
| Pectoral girdle scapular (shoulder bone) | Broad i.e. Flattened bladeglenoid cavity to articulate with humerusmetacromion/acromion for muscle attachmenthard to provide supportsocket with cartilage/smooth surface to reduce friction | Support Muscle attachment Articulates with humerus |
| Humerus | long shaft for muscle attachmentround head to articulate with glenoid cavitytrochlea for articulation with ulnaolecranon fosa to prevent arm bending the other way | movementmuscle attachment |
| Ulna and radius | ulna longer and on side of little fingerhas sigmoid notch and olecranon process to form hinge joint with humerusradius is smaller and lies along thumb side and does not join ulnaallows articulation with wrist bones | movementmuscle attachments |
| Pelvic girdle(hip bone) | composed of three fused bones (ilium, ischium, pubis)upper end fused to sacrumlower end has acetabalum for articulation with femurhas abturator foramen for passage of nerves and blood vessels | movementmuscle attachmentsupportabsorbs pressure exerted by ground when animal moves |
| Femur | rounded head to fit in acetabulum of pelvisprojections called trochanter for attachment of thigh musclescondyles at lower end for articulation with tibipatella that covers knee and prevents leg from bending backwards | movementmuscle attachment |
| Tibia and fibula | tibia is longer than fibulatibia is outer bone and fibula is inner bonetibia lies on side of large toefibula is fused to tibia (on outer side) | movementmuscle attachment |
- a) What is a joint?
- the point where bones meet
ii) State the functions of joints
- provide a point of articulation between bones
iii) Name the main types of joints
- immovable joints e.g. skull, pelvic girdles and sacrum
- slightly movable joints e.g. between vertebrae
- Freely movable joints e.g. knee, elbow
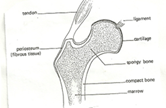
iv) Give the features of movable joints
- ends of bones covered with articular cartilage
- ends bound by capsules of ligaments
- have joint cavity filled with lubricating fluid called synovial fluid secreted by synovial membrane
- they are called synovial joints
b) Describe the synovial joints
- Ball and socket
- allow movement in all planes /directions i.e. 360o
- rounded end of bone fits into a rounded cavity in another bone
- e.g. shoulder joint and hip joint
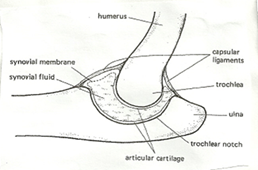
- Hinge joint
convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another bone
this allows movement in only one plane/direction 180o
e.g. elbow joint and knee joint
- Pivot joint
- allows rotation e.g. where atlas pivots on olecranon process of axis
c) i) What is synovial fluid?
- lubricating fluid produced by synovial membrane at movable joints
ii) State the functions of synovial fluid
- absorbs shock
- reduces friction/gives lubrication
- nourishment
- distributes pressure
- Explain the following terms
- Ligament
- connective tissue joining one bone to another
- Cartilage
- supporting soft tissue found at joints
- they cushion the bones and absorb shock
- Tendon
- tissue that connects muscle to bones
- Muscles
- i) What is a muscle?
- fleshy part of body
- composed of long cells enclosed in a sheath
- specialized cells capable of contracting
ii) State the functions of muscles
- cover the skeleton
- provide shape
- contract and relax to enable body to move
- Describe the structure and function of various types of muscles
- skeletal muscles
- also called voluntary/striated/stripped muscles
- they are attached to skeleton
- they consist of striated, multinucleated, ling fibers and are cylindrical shaped
- found on legs, arms, eyes, neck where they cause movement
- Involuntary muscles
- also called smooth/visceral/unstriated/unstripped
- their movement is not controlled by the will
- they are unstriated, nucleated, short fibred and spindle shaped
- are found in alimentary canal, blood vessels, secretory glands, other tubular visceral organs, bladder, uterus, urinary tract, reproductive system, respiratory tract, ciliary body, iris
- Cardiac muscles
- also called myocardium
- found in the walls of the heart
- are not under control of the will
- composed of long cylindrical cells with special junctions
- myogenic i.e. generate their own contraction
- they are not fatigued
- their function is contraction of the heart to pump blood
- Explain how muscles cause movement of the human arm
- the muscles which bring about these movements are called biceps and triceps
- biceps are attached to scapula and radius for bending
- triceps are attached to scapula, humerus and ulna for stretching
- when the biceps contracts, it pulls the radius (forearm) and the hand bends
- the triceps relaxes at the same time
- when the triceps contracts and biceps relaxes(extends) the arm is stretched
- biceps flexes the arm (flexor) and triceps extend(extensor muscle) the arm
- i) State the structural differences between skeletal muscles e.g. biceps and smooth muscles e.g. gut muscle
| Skeletal (biceps) | Smooth (gut) muscle |
| multinucleatedstriated/strippedlong muscle fibersblock/cylindrical | uninucleatedunstriatedshort muscle fibersspindle shaped |
ii) Name the cartilage found between the bones of the vertebral column
- intervertebral disc
- What are the functions of the cartilage named in (d) ii) above
- acts as a cushion/absorbs shock
- reduces friction
- flexibility of vertebral column
