- What are the functions of the human ear?
- hearing
- balancing
- How are the structures of the human ear suited to perform the function of hearing?
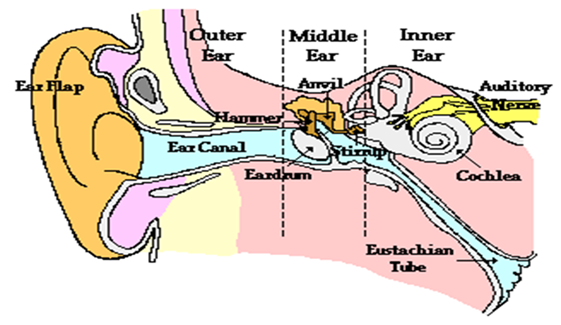
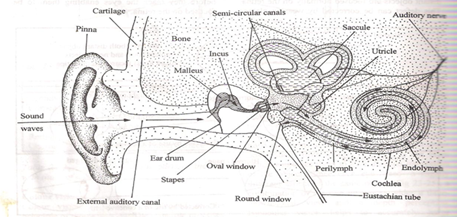
- shape of the external ear/pinna allows collection of sound waves and channels them down the auditory canal/auditory mateus
- auditory canal is a tube that concentrates and directs sound waves to tympanic membrane/ tympanum/eardrum
- Eardrum is thin and tight. It sets into vibration/vibrates/converts sound waves into vibrations
- the vibrations are transmitted to the ear ossicles/malleus, incus and stapes that amplify the sound vibrations
- the vibrations are then transmitted to the fennestra ovalis/oval window
- Oval window is a membrane which amplifies/transmits vibrations to the fluids (perilymph and endolymph) then to cochlea.
- The cochlea is coiled to occupy a small space and accommodate a large number of sensory cells
- The sensory cells/hairs (in the cochlea) are set into vibrations/stimulated producing nerve impulses in the auditory nerve
- Impulses in the auditory nerve are transmitted to the brain for interpretation for hearing
- Eustachian tube connects the inner ear to the throat. It equalizes air pressure in the middle ear with the atmospheric air pressure (in outer ear)
- Fennestra rotundus/round window dissipates/discharges/discards vibrations from inner ear to middle ear
iii) Explain how the structure of the human ear performs the function of balancing
- there are three semi-circular canals/utriculus/succulus/vestibular apparatus arranged in planes at right angles to each other
- at the end of each canal is a swelling called ampulla which contains receptors
- the movement of the head causes movement of the fluid/endolymph in at least one canal
- the fluid movement causes stimulation of the receptors/sensory hairs
- sensory impulses are generated
- the auditory nerve transmits the impulses to the brain for interpretation for the position of body/posture/balance
iv) State what would happen if the auditory nerve was completely damaged
- deafness
- loss of body balance
impulse not transmitted to the brain
