- How is the human eye adapted to its function?
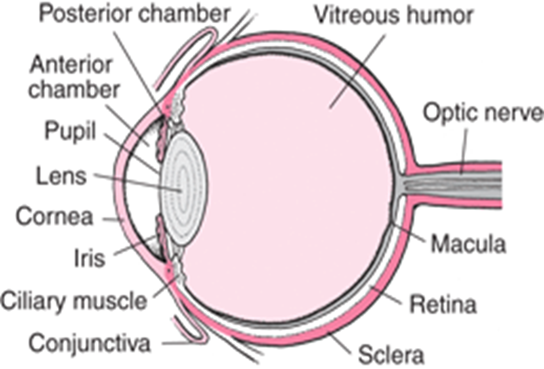
- conjunctiva is thin/transparent/tough to allow light to pass through/to protect the eye
- Sclerotic layer is made up of (collagen) fibers/fibrous. It maintains shape of the eyeball/protects the eye
- cornea is transparent/curved thus refracts light rays/allows light to pass through
- Choroid is a layer of tissue with black pigment/dark pigment. Prevents internal reflection of light in the eye/contains blood vessels that supply oxygen/nutrients/remove (metabolic) wastes from the eye
- retina has cones/rods for bright colour vision/low light vision
- yellow spot has a high concentration of cones for accurate vision/visual acuity
- Blind spot has no cones and rods. Place where optic nerve leaves/enters the eye
- optic nerve has (sensory) nerve fibers for transmission of impulses to the brain (for interpretation)
- Lens is biconvex/made up of elastic material/transparent. Adjust focus on far or near objects allow light to pass through/for refraction of light rays
- ciliary body is made up of muscle fibers/glandular which contract/relax to change shape
- suspensory ligaments are inelastic to hold lens in position/attach it to ciliary body
- iris(is the coloured part of the eye it) has radial and circular muscles which control size of pupil
- pupil is the small hole at the centre of iris through which light passes into the eye
- aqueous humor is a fluid through which oxygen/nutrients pass to the cornea/lens/maintains shape of the eyeball/refracts light rays
- vitreous humor is a fluid which maintains shape of eye/refracts light rays
iii) What is accommodation of the eye?
- ability of the eye to adjust to bring an image from a near or far object into sharp focus on the retina
iv) Explain how an eye viewing a near object adjusts to viewing a far object
- ciliary muscles relax
- suspensory ligaments become taut/tight
- lens decreases curvature/becomes thinner
- radial muscles relax
- circular muscles contract
- size of pupil decreases to reduce amount of light
v) What changes occur in the eye if it changes from observing an object at a distance to one at a closer range?
– ciliary muscles contract
– Tension in suspensory ligaments reduces/relax/ slackens
– Lens bulges/thickens/increases curvature
– Radial muscles contract
– Circular muscles relax
– Size of pupil becomes large to allow in more light.
- State the changes which would take place in the eye if a person in a dark room had lights switched on
- circular muscles contract and radial muscles relax
- pupil becomes small to allow less light into the eye
- Explain how the eye forms an image
- the mammalian eye works like a camera
- light rays enter the cornea pass through the pupil, aqueous humor, lens and vireous humor
- light rays are refracted by the aqueous and humor and lenses
- finally light falls on the retina to form an image
- the image is real and inverted and smaller than object, back to front/reversed
- Retina forms a fine image when light rays reach it.
- Name the defects of the eye and state how they can be corrected
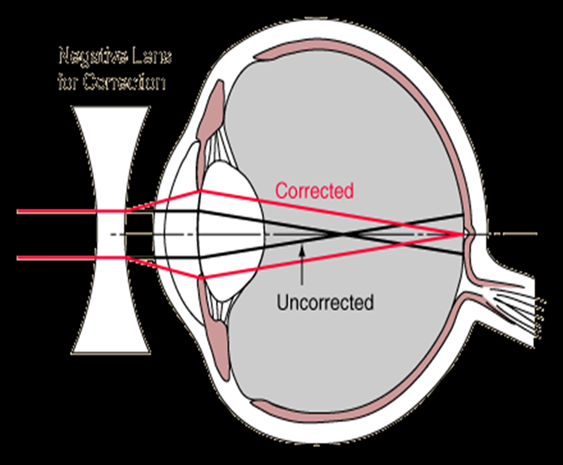
Short sight (Myopia)
- eye cannot focus on far objects
- image is formed in front of the retina because light rays converge in front of retina
- the lens is too thick, curve and eyeball too long
- corrected by wearing concave/biconcave/lenses
these lenses diverge light rays onto retina
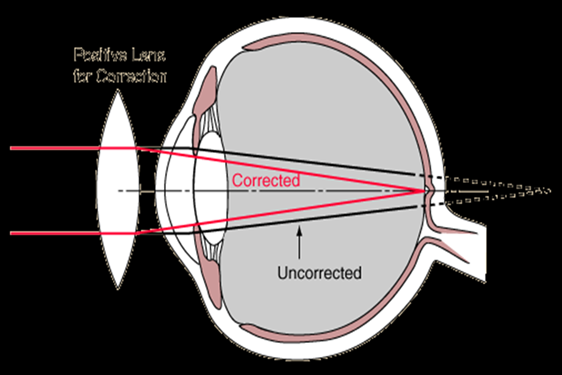
Long sight (Hypermetropia)
- eye lenses are unable to focus because they are flat, thin and weak hence unable to focus image on the retina
- they are unable to accommodate/change the focal length
- near image is formed behind the retina but a distant one is correctly focused on the retina
- corrected by wearing convex/biconvex/converging lenses
Presbyopia
- occurs in old age hence called old sight
- caused due to loss of elasticity of lenses, weakness of ciliary muscles hence lack of focus of light rays
- this causes long sight
- corrected by wearing biconvex/convex/converging lenses
Squinting
- eyeballs are uncoordinated/do not turn at the same time
- eye muscles move in different directions
- this makes accommodation and focusing difficult
- corrected through surgery
Astigmatism
- surface of cornea is uneven
- leads to weak focus of light raise on retina
- corrected by using cylindrical lenses/lenses with combined curvature
- State the advantages of having two eyes in human beings
- stereoscopic vision
- gives a wider angle of binocular vision
- if one is damaged human is not blinded
