CONTEMPORARY THEMES IN HISTORY AND CITIZENSHIP
Sub-Strand 4.1: Peace and Conflict Transformations in Kenya (8 Lessons)
- National Activities Promoting Peace in Kenya:
1. National Peace Building Initiatives:
- The National Cohesion and Integration Commission (NCIC).
- Peace education programs in schools.
- Interfaith dialogue and initiatives.
- Community peace forums.
- Cultural Festivals and Events: Promoting unity and understanding among diverse communities.
- Sports and Arts: Using sports and arts to foster social cohesion.
- National Holidays and Celebrations: Emphasizing national unity and patriotism.
- Media Campaigns: Promoting messages of peace and tolerance.
- Government Initiatives: Such as Huduma centers, to promote equal access to services.

Diverse group of Kenyans participating in a cultural festival
- The Constitution (2010) and Conflict Prevention:
- Chapter Four: Bill of Rights: Protecting fundamental rights and freedoms, ensuring equality and non-discrimination.
- Devolution: Distributing power and resources to county governments, reducing marginalization.
- Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC): Ensuring free, fair, and credible elections.
- National Land Commission (NLC): Addressing land disputes and promoting equitable land distribution.
- National Cohesion and Integration Commission (NCIC): Promoting national unity and combating ethnic discrimination.
- Chapter Ten: Values and Principles of Public Service: Promoting integrity and accountability in public service.
- The Judiciary: Providing fair and impartial conflict resolution.
Court room, representing the judicial system
- Incidences Where the Constitution Has Been Applied to Foster Peace:
- Post-Election Violence (2007/2008): The Constitution’s emphasis on devolution and electoral reforms aimed to address root causes.
- Land Disputes: The NLC has mediated land disputes, promoting peaceful resolution.
- Ethnic Conflicts: The NCIC has investigated and prosecuted hate speech, promoting national cohesion.
- Electoral Disputes: The Judiciary has adjudicated electoral disputes, upholding the rule of law.
- Implementation of Devolution: The creation of county governments has given local communities a greater sense of ownership.
- Protecting marginalized groups: The bill of rights has been used to protect the rights of minority groups.

People participating in a peaceful mediation process
- Upholding Peace and Curbing Conflicts:
- Promoting dialogue and reconciliation.
- Respecting diversity and promoting tolerance.
- Advocating for justice and equality.
- Reporting hate speech and incitement to violence.
- Participating in community peace initiatives.
- Upholding the rule of law.
- Educating others on the importance of peace. Practicing active listening and empathy.

People from different backgrounds engaged in dialogue
- Benefits of a Peaceful Nation:
- Economic Growth: Stable environment attracts investment and promotes trade.
- Social Development: Improved access to education, healthcare, and other services.
- Political Stability: Stronger democracy and rule of law.
- National Unity: Reduced ethnic and social divisions.
- Improved International Relations: Enhanced reputation and cooperation with other nations.
- Reduced human suffering. Increased tourism.
Example of a Role-Play Scenario:
- Scenario: A conflict arises between two communities over water resources.
Role-Play: Students enact a mediation process, involving community leaders, government officials, and affected residents, to find a peaceful solution.
Sub-Strand 4.2: The 4th Industrial and Technologies Revolution (9 Lessons)
- Tracing Technological Advancements in the 4th Generation:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Machine learning, natural language processing, robotics.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connected devices and sensors.
- Big Data and Analytics: Processing and analyzing vast amounts of data.
- Cloud Computing: On-demand access to computing resources.
- 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing.
- Biotechnology: Genetic engineering, personalized medicine.
- Nanotechnology: Manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular scale.
- Quantum Computing: A new era of computing power.
- 5G networks: Faster and more reliable connection. Autonomous Vehicles: Self driving cars.

Futuristic city with interconnected devices, representing the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Role of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the 4th Generation:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Enabling real-time monitoring and decisionmaking.
- Communication and Collaboration: Facilitating global connectivity and information sharing.
- Automation and Efficiency: Streamlining processes and reducing human error.
- Education and Knowledge Dissemination: Providing access to online learning resources.
- E-commerce and Digital Economy: Transforming business models and consumer behavior.
- Remote work: enabling people to work from anywhere.

People collaborating online, representing digital communication
- Impact of Technology in the 4th Generation:
- Positive Impacts:
- Increased efficiency and productivity.
- Improved communication and access to information.
- Advancements in healthcare and medicine.
- Creation of new jobs and industries.
- Enhanced sustainability through smart technologies.
- Negative Impacts:
- Job displacement due to automation.
- Increased digital divide and inequality.
- Privacy concerns and data security risks.
- Ethical dilemmas related to AI and biotechnology.
- Increased social isolation.
- Cyber-security threats.
- Positive Impacts:
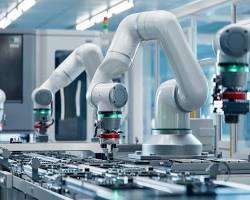
Factory with automated robots, representing the impact of automation
- Opportunities for Growth and Sustainability:
- Smart Cities: Using technology to improve urban infrastructure and services.
- Renewable Energy: Developing sustainable energy solutions.
- Precision Agriculture: Optimizing farming practices to reduce waste.
- E-learning and Online Education: Expanding access to quality education.
- Telemedicine: Providing remote healthcare services.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Reducing environmental impact through advanced technologies.

Drone monitoring crops, representing precision agriculture
- Technology and Historical Information:
- Digital Archives: Preservation and accessibility of historical documents.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive historical experiences.
- Online Databases: Access to vast amounts of historical data.
- Digital Humanities: Using technology to analyze and interpret historical information.
Computer Simulations: Recreating historical events and processes.
Download complete notes Grade 10 Notes Senior School 2026
