KCSE 2022
- Components of Business Studies. (4 Marks)
i) Accounting ii) Commerce iii) Economics iv) Entrepreneurship
- Limitation of direct trade. (4 Marks)
i) There is higher distribution costs ii) It is limited to few products/not applicable to most products
- Producer may experience challenges in storage of adequate stock
- Risks involved are borne by producer alone.
- Consumers may access few varieties of goods and services
- Consumers may get poor/low quality of goods and services
- Producer may experience challenges of transporting the goods.
- Producer will have to bear cost of preparing goods for sale.
- It may be difficult to reach to consumers especially if are widely spread
- Calculation for Compensation. (4 Marks)
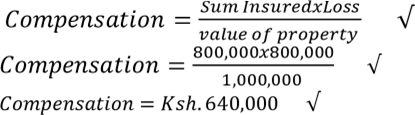
(b) –The house was under insured.
-The house was insured for Ksh. 800,000 instead of Ksh. 1,000,000
- Circular flow of income. (4 Marks)
- Firms
- Households
- Provision for factors of production
- Payment for goods and services
- Books of original entry
i) Purchases Journal/Creditors Journal/Bought journal ii) Sales Returns Journal/Returns Inwards Journal iii) Cash Receipt Journal/Cash book iv) General Journal/Journal proper
- Circumstances under which CWO would be preferred.
- Where the buyer is new to the seller.
- Where the buyer’s credit worthiness is in doubt. iii) Where CWO is the policy of the business.
- Where the seller is operating a mail order store business.
- Where the seller wants to avoid high cost of debt collection.
- Where the seller requires cash urgently
- Where the seller want to avoid a lot of record
keeping viii) Where the seller needs working capital/ready capital.
- Sources of government revenue other than tax. (4 Marks)
- Fines from courts
- License fees
- Borrowing loans
- Grants and foreign aid
- Rent and rates for use of government property
- Dividends and profits from government investments
- Proceeds from sale of government property
- Interest earned from loans advanced by government
- Escheats
- Ways in which economic environment may lead to business success.
- Increase in consumers income which increases their
purchasing power
- Increased government subsidies lowering cost of production
- Decrease in corporation tax encourage businesses to produce more
- Increase in personal income tax increases consumers
purchasing power
- Decrease in interest rates ensures consumers have money to spend on goods and services.
- Low rate of inflation encourages consumers to buy more
- Low exchange rates encourage foreign trade
- Price stability leading to predictable income
- Equitable distribution of income
9. Circumstances under which firm may be located near the market. (4 Marks)
- Where it is cheaper to transport finished goods than raw materials
- If the government requires so. iii) Where market is concentrated in one area.
- Where there is need to save on transportation costs of finished goods.
- Where the finished goods are highly perishable.vi) Where the finished goods are heavy and bulky.vii) Where the finished goods are fragileviii) Where level of competition is high so as to deal with consumers directly
- Meaning of term in Trends of Business Units. (4 Marks)
- Holding company-It is a company that acquires fifty one percent shares or more of another company.
- Amalgamation-This is where two or more businesses combine and form a one new business.
- Absorption-This is where one business buys all assets of another business and the bought business ceases to exist.
- Cartel-It is a group of related companies that agree to work together to control output and market for their products.
- Market structures. (4 Marks)
- Monopoly
- Perfect competition iii) Oligopoly iv) Monopolistic competition
- Causes of cost-push inflation. (4 Marks)
- Increase in wages and salariesii) Increase in indirect taxes such as VATiii) Reduction/ withdraw in subsidies by governmentiv) Increase of profit margin by businesses
v) Increase in cost of utilities such as electricityvi) Unfavourable government policies making it expensive to run business
vii) Occurrence of natural calamities such as floodviii) Increase in prices of raw materials
- Reasons for ethical practice in business. (4 Marks)
- To ensure fair competition in business ii) To protect environment/avoid environmental degradation/pollution
iii) To ensure there is no discrimination in business iv) To eliminate use of unfair means of achieving business objectives like selling underweight products.
v) To protect consumers from exploitation.vi) To ensure rights of workers/employees are upheldvii) To enhance the public image of the business
- Effects of transaction on balance sheet totals. (4 Marks)
i) No effect ii) Increase iii) Increase iv) Decrease
- Benefits of product promotion to the producer
(4 Marks)
i) To counter competitionii) To increase sales volume of a given product/expand marketiii) To create awareness about a productiv) To enhance customer loyalty
v) To persuade customers to try a new productvi) To remind customers about existence of a product in the marketvii) To avoid misinformation about a productviii) To improve the business image
- Types of unemployment. (4 Marks)
i) Seasonal unemploymentii) Cyclical unemploymentiii) Disguised/hidden unemploymentiv) Voluntary/Real wage unemployment
- Differences between primary wants and secondary wants
(4 Marks)
| Primary wants | Secondary wants |
| One cannot do without them | One can do without them |
| They cannot be postponed | They can be postponed |
| They are felt needs | They are desired needs |
| They are universal | They are not universal |
| They are satisfied before secondary wants | They are satisfied after primary wants |
18. Net worth of a Business (Capital Invested) (4 Marks)
𝑁𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ/𝐶𝑎𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐼𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑒𝑑 = 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 − 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠 √
𝑁𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ = (40,000 + 60,000 + 12,000 + 16,000) − (24,000 + 18,000) √
𝑁𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ = 128,000 − 42,000 √
𝑁𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑡ℎ = 𝐾𝑠ℎ.86,000 √
19. Reasons why government protect consumers. (4 Marks)
- To ensure that products offered for sale are of good quality.
- To ensure that products offered for sale are of right quantity.
- To ensure health standards are maintained for good health of consumers.
- To ensured consumers are not overcharged.
- To ensure building construction and safety standards are maintained to avoid loss of lives and property in case they collapse. vi) To protect consumers from false advertising by traders who may give false information.
vii) To protect consumers from sale of harmful products that may adversely affect their health. viii) To protect consumers against breach of contract from traders who may fail to honour terms and conditions of sale.
ix) To ensure traders do not hoard products causing artificial shortage/ensure commodities are readily available to consumers.
- Types of financial institutions. (4 Marks)
i) Commercial banks ii) Savings and Credit Co-operatives Societies/SACCOS iii) Housing Finance companies iv) Development Banks/Development Finance institutions
- Benefits of electronic filing. (4 Marks)
- Requires little space/saves on office space as files are saved electronically
- Easier and fast to operate iii) More flexible/adaptable to future changes iv) Relatively cheap /saves on labour as few workers are involved
v) Enhance security as documents are protected with passwords vi) Reduces paper work vii) Enhance tidiness/neatness in an office viii) Enhance easy retrieval of documents ix) Provides for back-up system
x) Documents can be accessed through internet xi) It can be used to store large amount of information/wide storage
22. Benefits Kenya get by being member of EAC. (4 Marks)
i) Kenya get access to wide market for her products. ii) Enables Kenya to dispose off surplus products
Her citizen can gets employment opportunities from members of EAC
Kenya can specialize in producing what it has comparative advantage
Promotes peace and good relationship among members of EAC.
Can get products she does not produce at lower costs from members of EAC.
Enables movements of factors of production such as labour viii) Facilitates transfer of technology among EAC members
- Financial ratios. (4 Marks)

√
- Reasons for locating bonded warehouses at border points. (4 Marks)
- To ease collection of custom duties by the government.
- To ease inspection of imported products by the government.
- To ease re-exportation of goods when necessary. iv) To ease inspection of goods before they are exported. v) To save on transportation costs to the bonded warehouses.
vi) To avoid entry or exit of illegal goods into the countryvii) To control the quality of goods entering the country.viii) To control the quantities of goods entering the country.
ix) To avoid dumping of products into the country
25. Services offered by retailers to consumers. (4 Marks)
i) They offer credit facilities to consumers. ii) They offer after-sale services such as transportation iii) They stock variety of goods and services iv) They offer advice and information about the product
- They break bulk/ divide commodities to small quantities convenient to consumers.
- They avail commodities to places convenient for consumers.
- Ensure steady supply of products leading to stable prices viii) They prepare goods for sale such as sorting, grading
